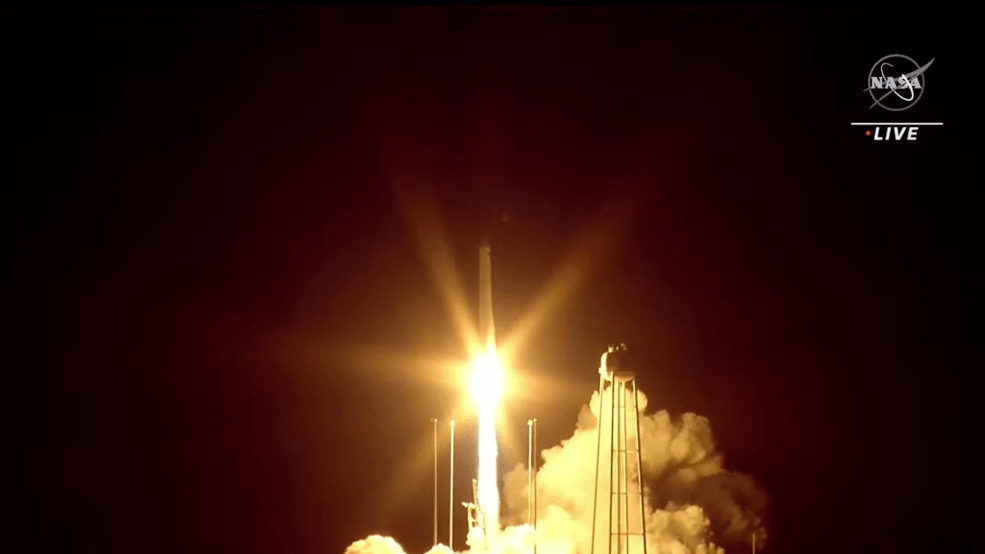
A Northrop Grumman Cygnus resupply spacecraft is on its way to the International Space Station with more than 8,200 pounds of NASA science investigations and cargo after launching at 8:31 p.m. EDT Tuesday from the agency’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia.
A Northrop Grumman Cygnus resupply spacecraft is on its way to the International Space Station with more than 8,200 pounds of NASA science investigations and cargo after launching at 8:31 p.m. EDT Tuesday from the agency’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia.
NASA Television, the NASA app, and the agency’s website will provide live coverage of the spacecraft’s rendezvous with the space station beginning at 4:30 a.m. Friday, Aug. 4.
Cygnus is scheduled for capture by the Canadarm2 robotic arm at 5:55 a.m., which will be operated by NASA astronaut Woody Hoburg with assistance from NASA astronaut Frank Rubio.
Installation coverage will resume at 7:30 a.m. Watch all events at:
Northrop Grumman’s 19th cargo flight to the space station is the eighth under its Commercial Resupply Services 2 contract with NASA. The Cygnus spacecraft launched on the company’s Antares 230+ rocket from the Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport’s Pad-0A on Wallops Island.
The resupply mission will support dozens of research experiments conducted during Expedition 69. Included among the investigations are:
- Testing gene therapy: Neuronix, sponsored by the International Space Station National Laboratory, demonstrates the formation of 3D neuron cell cultures in microgravity and tests a neuron-specific gene therapy.
- Experimenting with fire: The sixth Spacecraft Fire Experiments (Saffire-VI) is the last in a series to test flammability at different oxygen levels and to demonstrate fire detection and monitoring as well as post-fire cleanup capabilities. This experiment will take place after the spacecraft has departed the space station.
- Measuring atmospheric density: The Multi Needle Langmuir Probe, an investigation from ESA (European Space Agency), monitors plasma densities in the ionosphere – where Earth’s atmosphere meets space.
- Better water for explorers: A water system launched in fall 2008 provides water for crew consumption and food preparation on the space station. A new system, Exploration PWD, uses advanced water sanitization and microbial growth reduction methods and dispenses hot water.
- High-flying art: For I-Space Essay, JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) is sending a memory card that contains digital works created by students, such as pictures and poetry, to the space station.
- Robotic helper: A cube-shaped Astrobee robot is on its way back to the space station to help reduce the amount of time astronauts spend on routine tasks.
Hardware upgrades to improve outcomes for researchers
Cygnus also will deliver a condensation module and heat transfer system for the Flow Boiling and Condensation Experiment that will help researchers better understand heat distribution and flow. Such knowledge could be used to enhance mechanisms that protect astronauts from the extreme hot and cold temperatures of space.
The station’s Cold Atom Lab, which makes use of the microgravity environment of space to study quantum phenomena in ways that aren’t possible on Earth, will get an upgrade that will give scientists more data in a wider variety of experimental conditions.
These are just a sample of the hundreds of investigations conducted aboard the orbiting laboratory in the areas of biology and biotechnology, physical sciences, and Earth and space science. Such research benefits humanity and lays the groundwork for future human exploration through the agency’s Artemis missions, which will send astronauts to the Moon to prepare for future expeditions to Mars.
Northrop Grumman named the Cygnus ‘S.S. Laurel Clark’ after late NASA astronaut and crew member of NASA’s STS-107 mission aboard space shuttle Columbia, Laurel Clark.
The Cygnus spacecraft will remain at the space station until October before it departs and disposes of several thousand pounds of trash through its destructive re-entry into Earth’s atmosphere.
Learn more about Northrop Grumman’s mission at:
https://www.nasa.gov/northropgrumman/
-end-
Joshua Finch
Headquarters, Washington
202-358-1100
joshua.a.finch@nasa.gov
Sandra Jones
Johnson Space Center, Houston
281-483-5111
sandra.p.jones@nasa.gov
Amy Barra
Wallops Flight Facility, Virginia
757-824-1579
amy.l.barra@nasa.gov