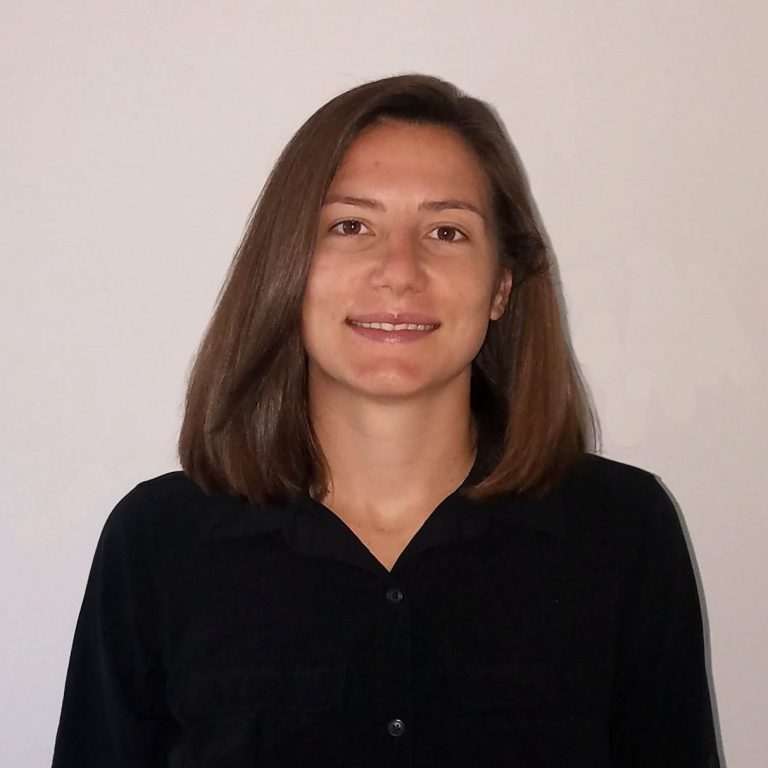
Amanda Saravia-Butler
Science Lead, GeneLab; NASA Open Science Data Repository (OSDR)
E-mail: amanda.m.saravia-butler@nasa.gov
Affiliation: KBR; Space Biosciences Research Branch
Biography
Dr. Amanda Saravia-Butler is a molecular biologist turned bioinformatician currently working on the GeneLab project at NASA Ames Research Center as the Science and Data Processing Lead. Originally from upstate New York, Amanda received her Bachelor’s degrees in Biology, Chemistry, and Mathematics from Utica College in Utica, NY. As an undergraduate student, she performed microbiology research to help discover a new species of bacteria. Amanda went on to earn her Ph.D. in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology with a concentration in Cancer Biology from the Mayo Clinic, where she identified and characterized novel molecular targets to treat pancreatic cancer. After completing graduate school, Amanda worked as a postdoctoral associate at the University of Miami studying early germ line development. In September 2017 she started at NASA Ames Research Center as a Mission Scientist on the Rodent Research project. Amanda began transitioning to GeneLab in May 2018 and has been working on the GeneLab project full time since then. In 2020, Amanda helped initiate, and currently leads, GeneLab for Colleges and Universities (GL4U), which provides space biology-relevant training in bioinformatics to both students and educators using compute platforms including SMCE and NSF ACCESS. Outside of work, Amanda volunteers her time to help organize and host seminars, professional development events, outreach activities, and networking events as part of the Ames Early Career Network (ECN), where she is currently the president and servers as the chair of the seminar series and outreach committees.
Education
Ph.D. Biochemistry and Molecular Biology; Concentration in Cancer Biology, Mayo Clinic Graduate School, 2014
B.S. Biology; B.S. Chemistry; M.A. Mathematics, Utica College, 2009
Select Honors, Awards, and Grants
- 2023, KBR One Award: In recognition of outstanding performance & Commitment to Excellence
- 2020, XSEDE: COVID-19 HPC Consortium – NASA Supercomputer Resources
- 2020, FILMSS Star Award for Leadership, Technical Contribution, and Teams Relations
- 2020, NASA Ames Group/Teams Honor Award for the GeneLab project
- 2019, ARC Space Biology Project Appreciation Award
- 2019, NASA Space Biology PPBE Grant
- 2018, NASA Group Achievement Award (Rodent Research Project Team)
- 2014, MBL Xenopus Genome Editing Workshop Scholarship
- 2012-2014, NIH F31 Pre-Doctoral Fellowship
- 2013, MBL Frontiers in SCs and Regeneration Scholarship
- 2012, Mayo Clinic Above and Beyond Award
Professional Links
Select Publications
- Sanders LM, Chok H, Samson F, Acuna AU, Lai Polo S-H, Boyko V, Chen Y-C, Dinh M, Gebre S, Galazka JM, Costes SV, and Saravia-Butler AM (2023). Batch effect correction methods for NASA GeneLab transcriptomic datasets. Frontiers in Astronomy and Space Sciences. doi.org/10.3389/fspas.2023.1200132.
- Saravia-Butler AM, Schisler JC, Taylor D, Beheshti A, Butler D, Meydan C, Foox J, Hernandez K, Mozsary C, Mason CE, and Meller R. (2022). Host transcriptional responses in nasal swabs identify potential SARS-CoV-2 infection in PCR negative patients. iScience. 25(11):105310.
- McDonald, J.T., Enguita, F.J., Taylor, D., Griffin, R.J., Priebe, W., Emmett, M.R., Sajadi, M.M., Harris, A.D., Clement, J., Dybas, J.M., Aykin-Burns, N., Guarnieri, J.W., Singh, L.N., Grabham, P., Baylin, S.B., Yousey, A., Pearson, A.N., Corry, P.M., Saravia-Butler, A., et al. (2021). Role of miR-2392 in driving SARS-CoV-2 infection. Cell Rep. 37(3):109839.
- *Overbey, E.G., *Saravia-Butler, A.M., et al. (2021). NASA GeneLab RNA-Seq Consensus Pipeline: Standardized Processing of Short-Read RNA-Seq Data. iScience. 24(4):102361. *Co-first authors.
- *Polo, S.L., *Saravia-Butler, A.M., Boyko, V., Dinh, M.T., Chen, Y., Fogle, H., Reinsch, S.S., Ray, S., Chakravarty, K., Marcu, O., Chen, R.B., Costes, S.V., and Galazka, J.M. (2020). RNAseq analysis of rodent spaceflight experiments is confounded by sample collection techniques. iScience. 23(12):101733. *Co-first authors.
- Choi, S.Y., Saravia-Butler, A.M., Shirazi-Fard, Y., Leveson-Gower, D., Stodieck, L.S., Cadena, S.M., Beegle, J., Solis, S., Ronca, A., and Globus, R.K. (2020). Validation of a New Rodent Experimental System to Investigate Consequences of Long Duration Space Habitation. Scientific Reports. 10:2336.
- Butler, A.M., Owens, D.A., King, M.L., and Aguero, T. (2019). Methods for Isolating the Balbiani Body / Germplasm from Xenopus laevis Oocytes. In: Pelegri F. (eds) Vertebrate Embryogenesis. Methods in Molecular Biology. 1920:265-275.
- Butler, A.M., Owens, D.A., Lingyu, W., and King, M.L. (2018). A novel role for sox7 in Xenopus early primordial germ cell development: mining the PGG transcriptome. Development. 145(1): dev155978.
- Owens, D.A., Butler, A.M., Aguero, T., Newman, K.M., Van Booven, D., and King, M.L. (2017). High-throughput analysis reveals novel maternal germline RNAs crucial for primordial germ cell preservation and proper migration. Development. 144(2):292-304.
- Butler, A.M., Aguero, T., Newman, K.M., and King, M.L. (2016). Primordial germ cell isolation from Xenopus laevis embryos. Methods in Molecular Biology. 1463:115-124.
- Butler, A.M., Scotti-Buzhardt, M.L., Erdogan, E., Li, S., Smith, K.E., Fields, A.P., and Murray, N.R. (2015). A small molecule inhibitor of atypical protein kinase C signaling inhibits pancreatic cancer transformed growth and invasion. Oncotarget. 6(17):15297-310.
- Butler, A.M., Scotti-Buzhardt, M.L., Li, S., Smith, K.E., Fields, A.P., and Murray, N.R. (2013). Protein kinase C zeta regulates human pancreatic cancer cell transformed growth and invasion through a STAT3-dependent mechanism. PLoS One. 8(8): e72061.