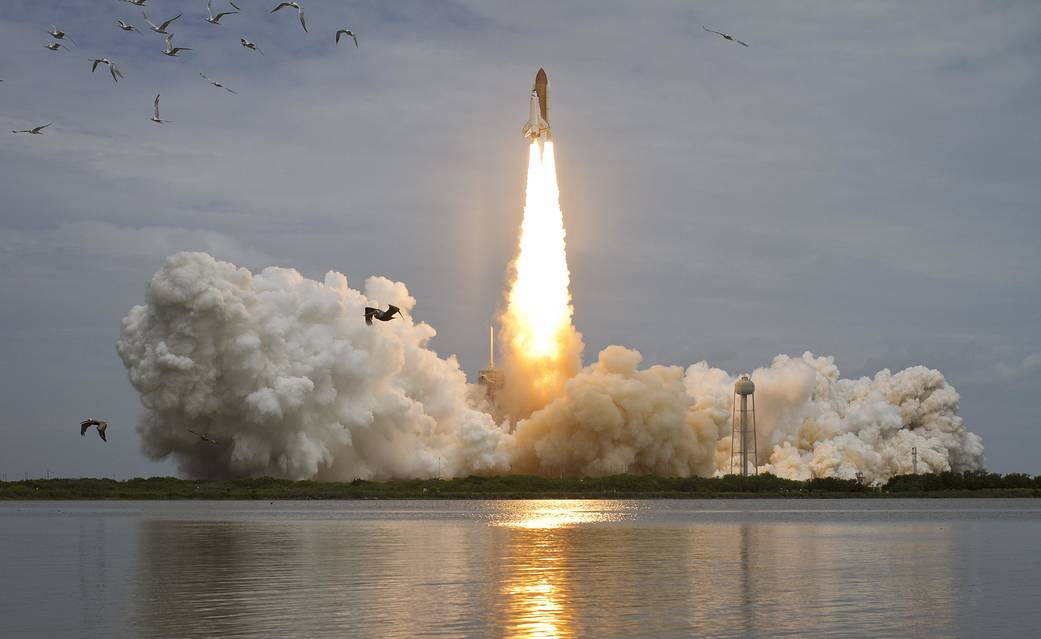
STS-2
Second test flight of the Space Shuttle to demonstrate safe re-launch and safe return of the orbiter and crew.
Orbiter
Mission Duration
Launch
Landing

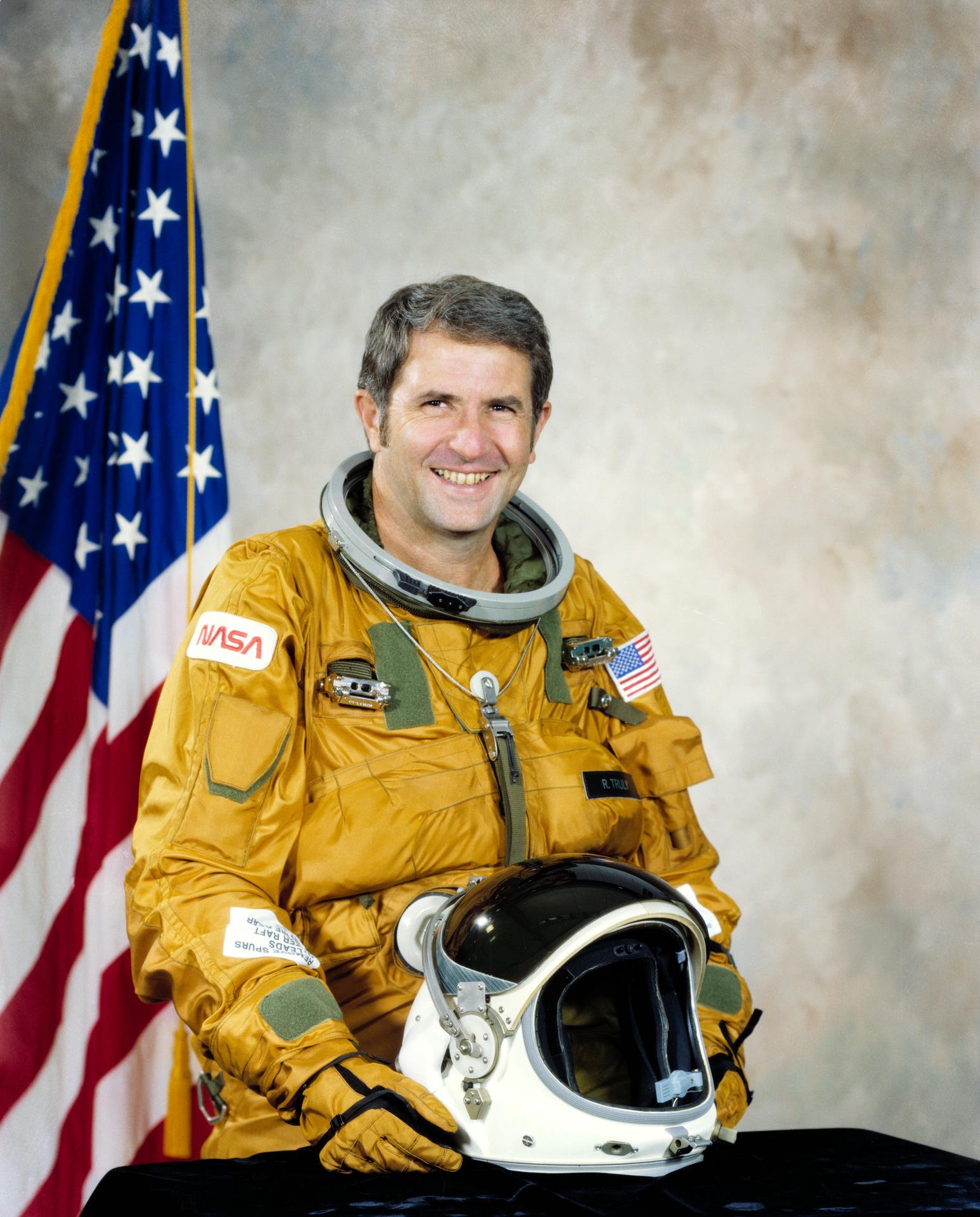
Joe H. Engle
Commander
An accomplished test pilot, Joe. H. Engle flew the X-15 above the threshold to qualify as an astronaut in 1965 and was later chosen for NASA’s 5th astronaut class in 1966. On his first space flight for STS-2, he became the first and only pilot to manually fly an aerospace vehicle from Mach 25 to landing.
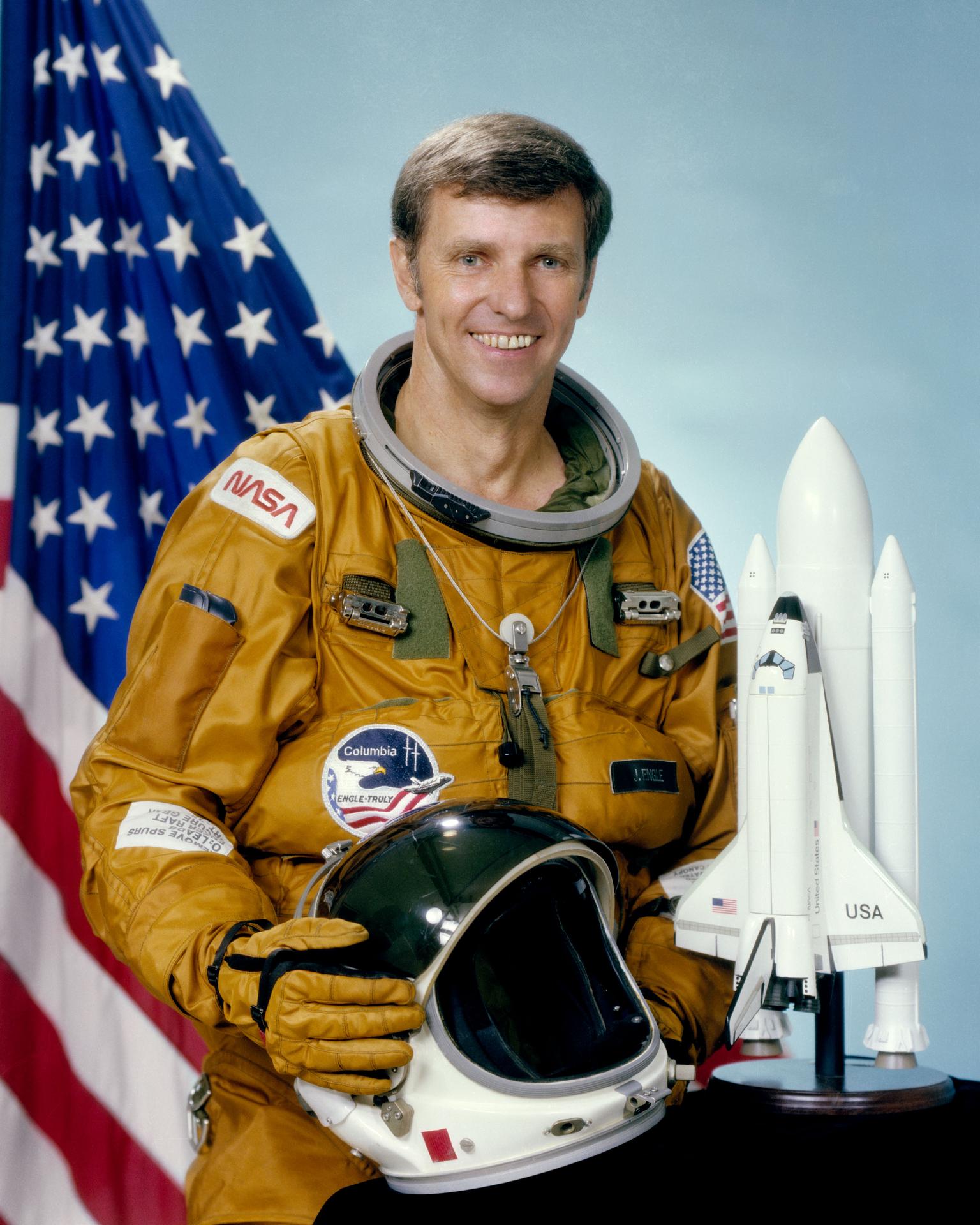

Richard H. Truly
Pilot
After serving as capsule communicator for all three Skylab missions in 1973 and the Apollo-Soyuz mission in 1975, Astronaut Richard H. Truly made his first space flight in November 1981 for STS-2.

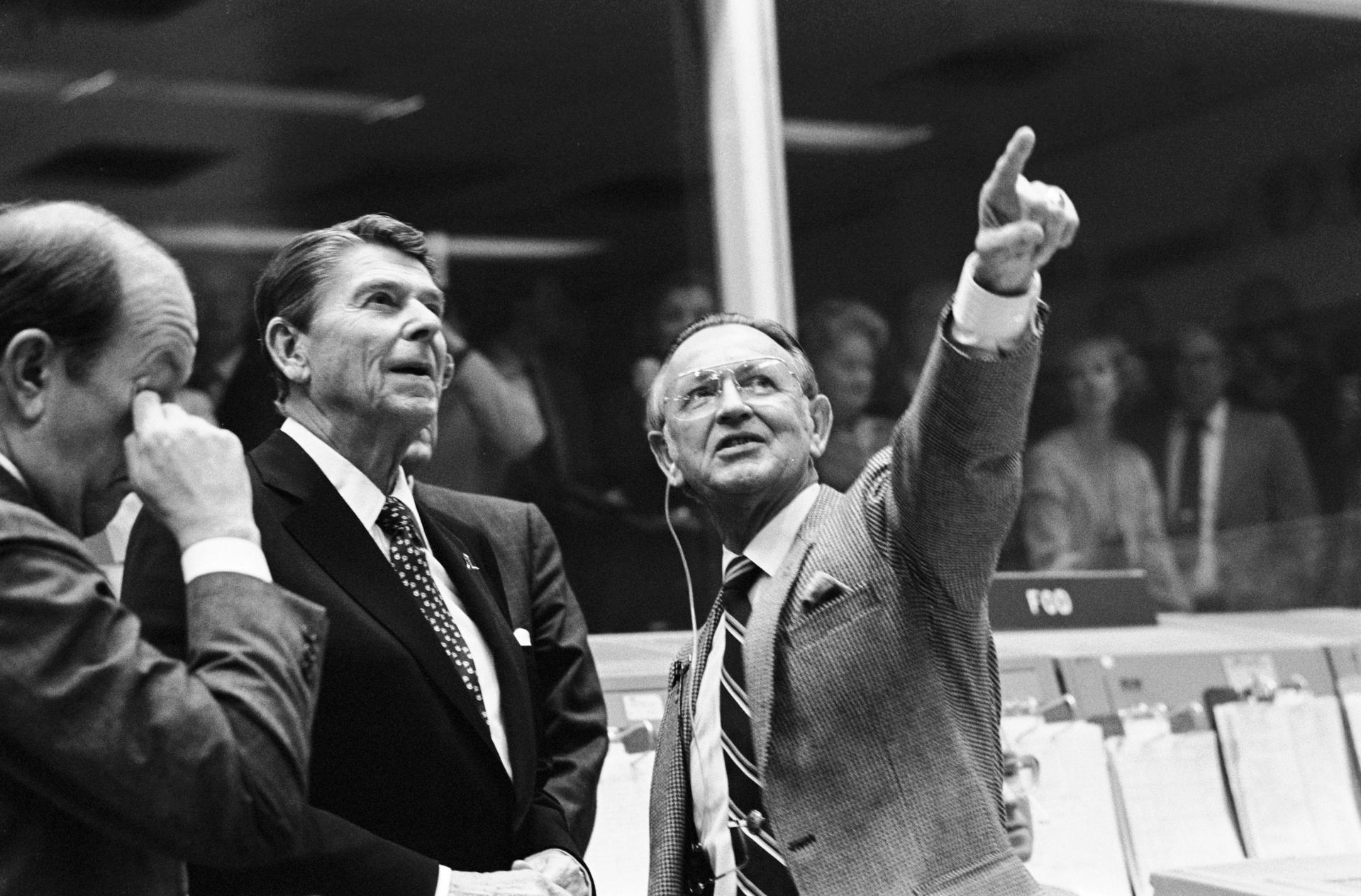
40 Years Ago: Columbia Returns to Space on the STS-2 Mission
Following a launch scrub a week earlier, space shuttle Columbia took to the skies on Nov. 12, 1981, for its…
Read the Story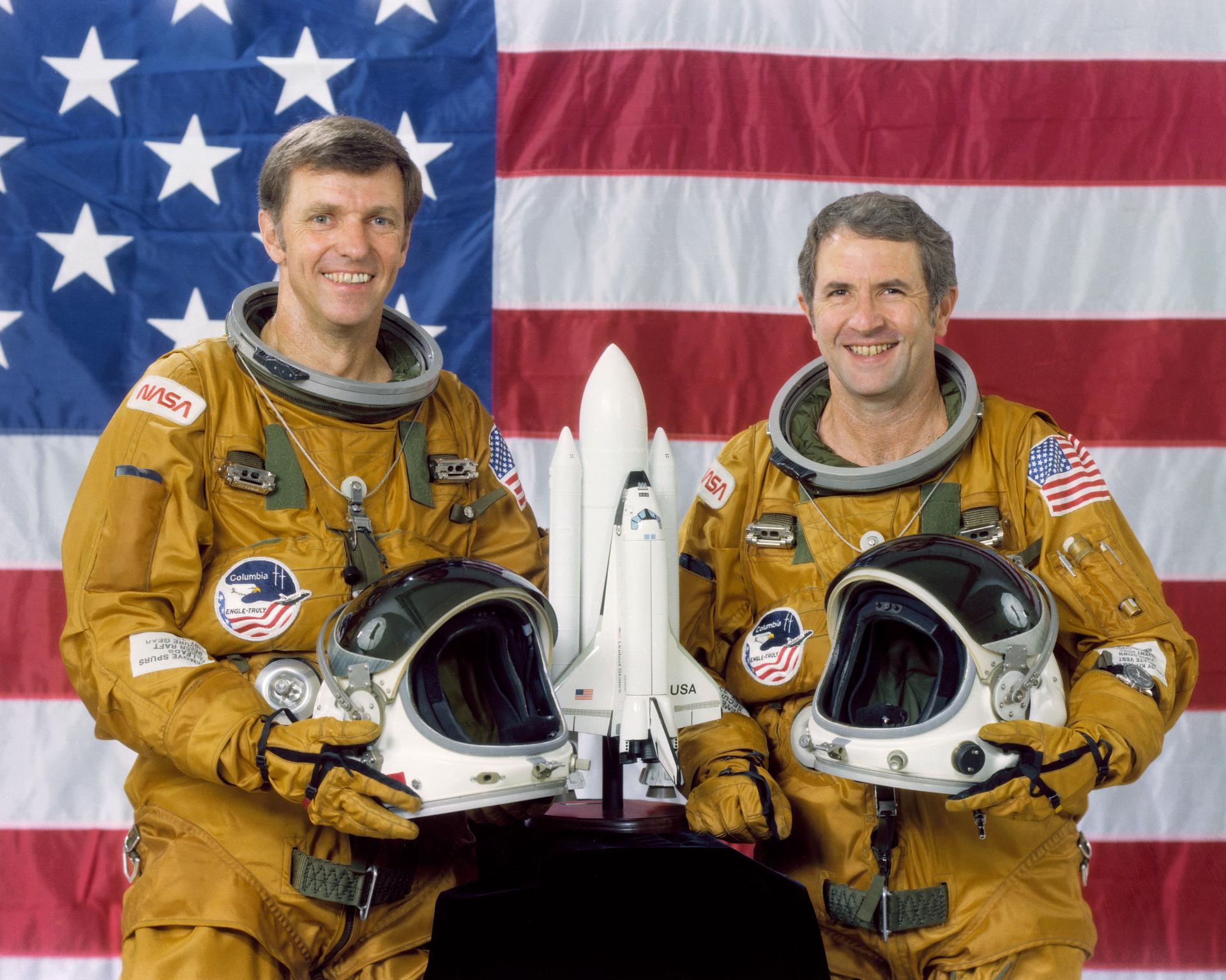
Mission: Second Shuttle Mission/Office of Space and Terrestrial Applications-1 (OSTA-1)
Space Shuttle: Columbia
Launch Pad: 39A
Launched: Nov. 12, 1981 at 10:09:59 a.m. EST
Launch Weight: 320,708 pounds
Landing Site: Edwards Air Force Base, Calif.
Landing: Nov. 14, 1981 at 1:23:11 p.m. PST
Runway: 23
Rollout Distance: 7,711 feet
Rollout Time: 53 seconds
Revolution: 37
Mission Duration: 2 days, 6 hours, 13 minutes and 12 seconds
Returned to KSC: Nov. 25, 1981
Orbit Altitude: 157 nautical miles
Orbit Inclination: 38.0 degrees
Miles Traveled: 1.075 million
Mission Objectives
Demonstrate safe re-launch and safe return of the orbiter and crew. Verify the combined performance of the entire shuttle vehicle – orbiter, solid rocket boosters and external tank.
Payloads included the Orbital Flight Test Pallet consisting of the Measurement of Air Pollution from Satellite (MAPS) experiment, the Shuttle Multispectral Infrared Radiometer (SMIRR) experiment, the Shuttle Imaging Radar (SIR-A) experiment, the Features Identification and Location Experiment (FILE) and the Ocean Color Experiment (OCE). Also included was the 11,048 lb. Development Flight Instrumentation (DFI) pallet, the Aerodynamic Coefficient Identification Package (ACIP), the Induced Environment Contamination Monitor (IECM) and the 5,395 lb. Office of Space and Terrestrial Applications Pallet (OSTA-1).
Mission Highlights
Launch originally set for Oct. 9 was rescheduled when a nitrogen tetroxide spill occurred during loading of the forward reaction control system. The launch scheduled for Nov. 4 delayed and then scrubbed when the countdown computer called for hold in the count due to an apparent low reading on fuel cell oxygen tank pressures. During the hold, high oil pressures were discovered in two of three auxiliary power units (APUs) that operate hydraulic system. APU gear boxes needed to be flushed and filters replaced, forcing the launch to reschedule. The launch on Nov. 12 delayed two hours, 40 minutes to replace the multiplexer/demultiplexer and additional nine minutes, 59 seconds to review systems status.
Modifications of the water sound suppression system at the pad to absorb the solid rocket booster overpressure wave during launch were effective—no tiles were lost and only 12 were damaged.
The planned five-day mission was cut nearly three days due to failure of one of three fuel cells that produce electricity and drinking water, but 90 percent of mission objectives achieved, including first time remote manipulator system tests. Mission scientists were satisfied with data received from Office of Space and Terrestrial Applications-1 (OSTA-1) Earth observation experiments mounted on Spacelab pallet in payload bay.
Latest STS-2 Articles
Stay up-to-date with the latest content from NASA as we explore the universe and discover more about our home planet.

On March 16, 1978, NASA formally announced the crews for the first four space shuttle missions. The four two-man crews…

Following a launch scrub a week earlier, space shuttle Columbia took to the skies on Nov. 12, 1981, for its…

As October 1981 drew to a close, the planned Nov. 4 launch of space shuttle Columbia on the STS-2 mission…

By the middle of October 1981, ground crews had completed repairs to Columbia after an oxidizer spill damaged the space…

Space shuttle Columbia arrived on Launch Pad 39A on Aug. 31, 1981, where ground crews prepared it for its second…

Following the Aug. 31, 1981 rollout of space shuttle Columbia to Launch Pad 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center (KSC)…