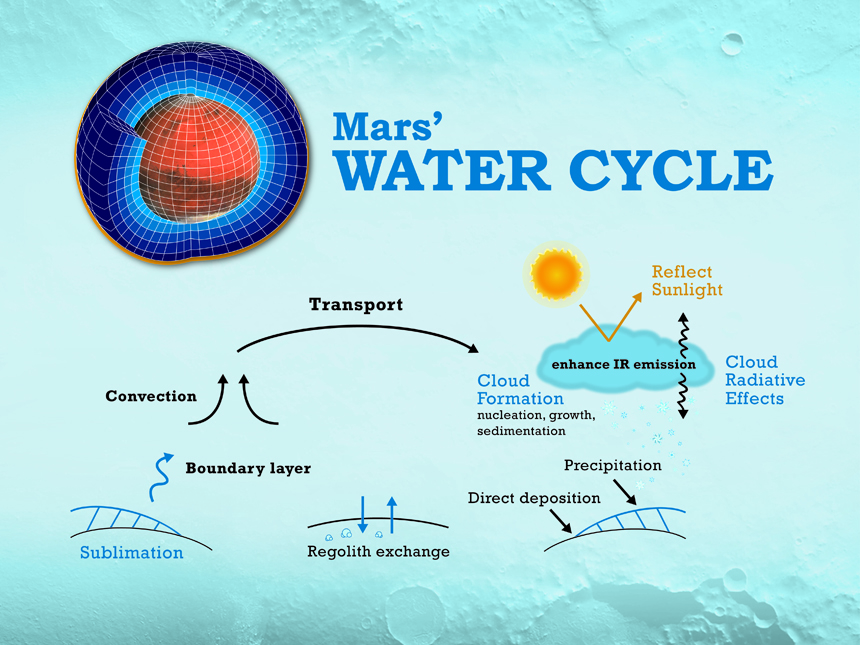
Water Cycle
On Mars, the main source of atmospheric water is the north residual water ice cap, which is exposed when the CO2 ice sublimates in northern summer. Water sublimates off of the north residual cap, producing the annual local maximum in atmospheric water vapor at high northern latitudes during summertime. This water is mixed and transported in the atmosphere before being deposited back to the surface as either frost or snow.
Water ice clouds can form in the presence of atmospheric dust when cloud nucleation and condensation is thermodynamically favored. These clouds affect the radiative balance of the atmosphere and tend to cool or warm the atmosphere and surface depending on their location and altitude. Although the north residual cap is likely the most important source for water on Mars today, other sources may play a role as well. For example, the regolith may adsorb and release water on daily or possibly seasonal timescales.
We use the NASA Ames Mars GCM to address several questions relating to the water cycle and how water ice clouds affect the climate of Mars. Click the links below to learn about our current water cycle projects.
Water Ice Clouds in Hellas Basin During Northern Hemisphere Summer