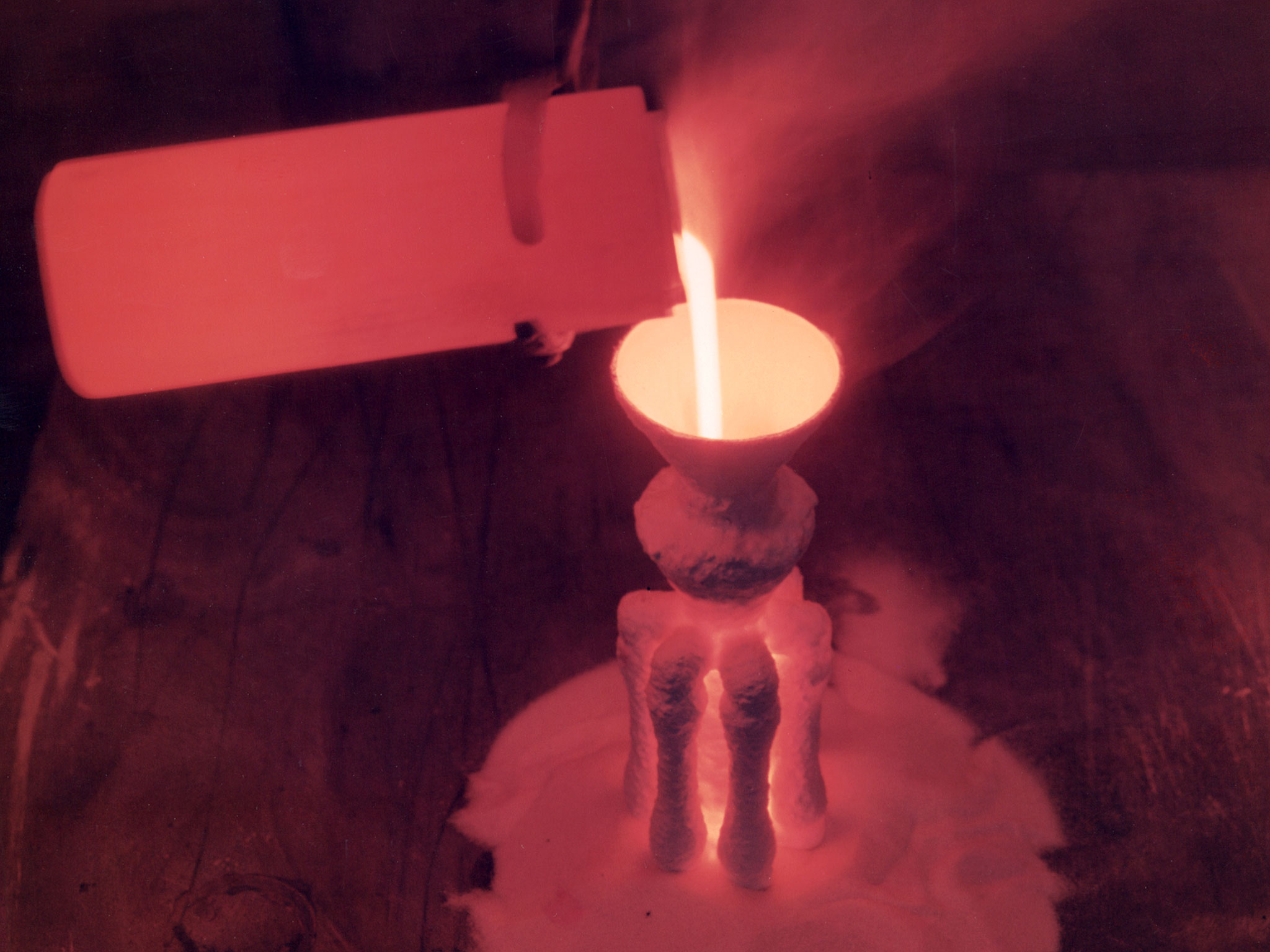
NASA Lewis Nickel Alloy being Poured in the Technical Service Building
A nickel alloy developed at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center being poured in a shop inside the Technical Services Building. Materials technology is an important element in the successful development of both advanced airbreathing and rocket propulsion systems. An array of dependable materials is needed to build different types of engines for operation in diverse environments. NASA Lewis began investigating the characteristics of different materials shortly after World War II. In 1949 the materials research group was expanded into its own division. The Lewis researchers studied and tested materials in environments that simulated the environment in which they would operate. Lewis created two programs in the early 1960s to create materials for new airbreathing engines. One concentrated on high-temperature alloys and the other on cooling turbine blades. William Klopp, Peter Raffo, Lester Rubenstein, and Walter Witzke developed Tungsten RHC, the highest strength metal at temperatures over 3500⁰ F. The men received an IR-100 Award for their efforts. Similarly a cobalt-tungsten alloy was developed by the Fatigue and Alloys Research Branch. The result was a combination of high temperature strength and magnetic properties that were applicable for generator rotor application. John Freche invented and patented a nickel alloy while searching for high temperature metals for aerospace use. NASA agreed to a three-year deal which granted Union Carbide exclusive use of the new alloy before it became public property.
- X