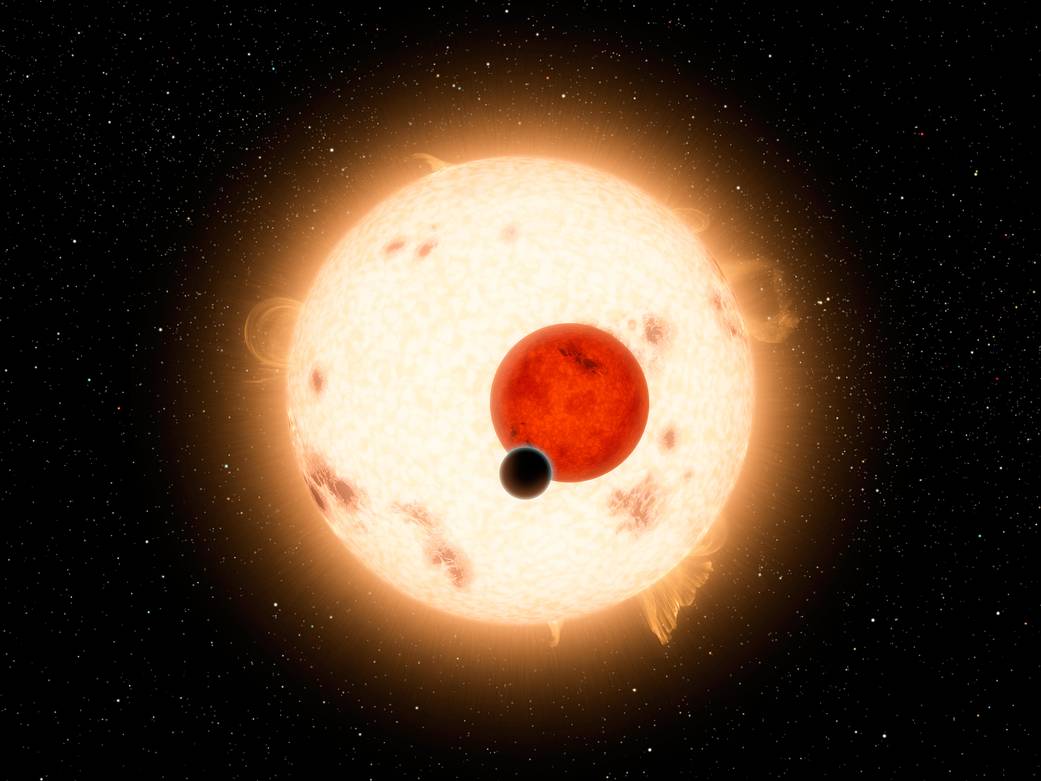
NASA’s Kepler mission has discovered a world where two suns set over the horizon instead of just one. The planet, called Kepler-16b, is the most “Tatooine-like” planet yet found in our galaxy and is depicted here in this artist’s concept with its two stars. Tatooine is the name of Luke Skywalker’s home world in the science fiction movie Star Wars. In this case, the planet is not thought to be habitable. It is a cold world, with a gaseous surface, but like Tatooine, it circles two stars. The largest of the two stars, a K dwarf, is about 69 percent the mass of our sun, and the smallest, a red dwarf, is about 20 percent the sun’s mass.
Most of what we know about the size of stars comes from pairs of stars that are oriented toward Earth in such a way that they are seen to eclipse each other. These star pairs are called eclipsing binaries. In addition, virtually all that we know about the size of planets around other stars comes from their transits across their stars. The Kepler-16 system combines the best of both worlds with planetary transits across an eclipsing binary system. This makes Kepler-16b one of the best-measured planets outside our solar system.
Kepler-16 orbits a slowly rotating K-dwarf that is, nevertheless, very active with numerous star spots. Its other parent star is a small red dwarf. The planetary orbital plane is aligned within half a degree of the stellar binary orbital plane. All these features combine to make Kepler-16 of major interest to studies of planet formation as well as astrophysics.
Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/R. Hurt