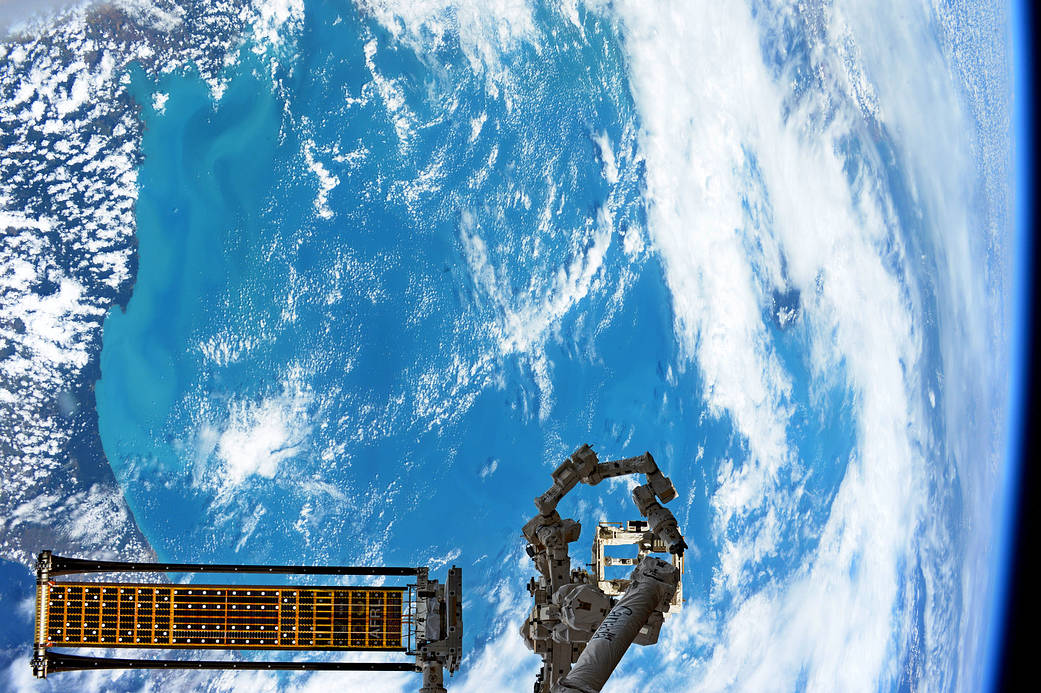
Unfurling much like a party horn on New Year’s, the Roll Out Solar Array (ROSA) experiment is deployed by the International Space Station’s Canadarm2 robotic arm on June 18, 2017.
Traditional solar panels used to power satellites can be bulky with heavy panels folded together using mechanical hinges. This new solar array’s design rolls up to form a compact cylinder for launch with significantly less mass and volume, potentially offering substantial cost savings as well as an increase in power for satellites.
ROSA was developed as part of the Solar Electric Propulsion project sponsored by NASA’s Space Technology Mission Directorate. NASA tested the ROSA technology in vacuum chambers on Earth several years ago, and this is its first test in space. This solar array technology was developed to power large spacecraft using highly-efficient electric propulsion on missions to deep space including Mars and the moon.
Image Credit: NASA