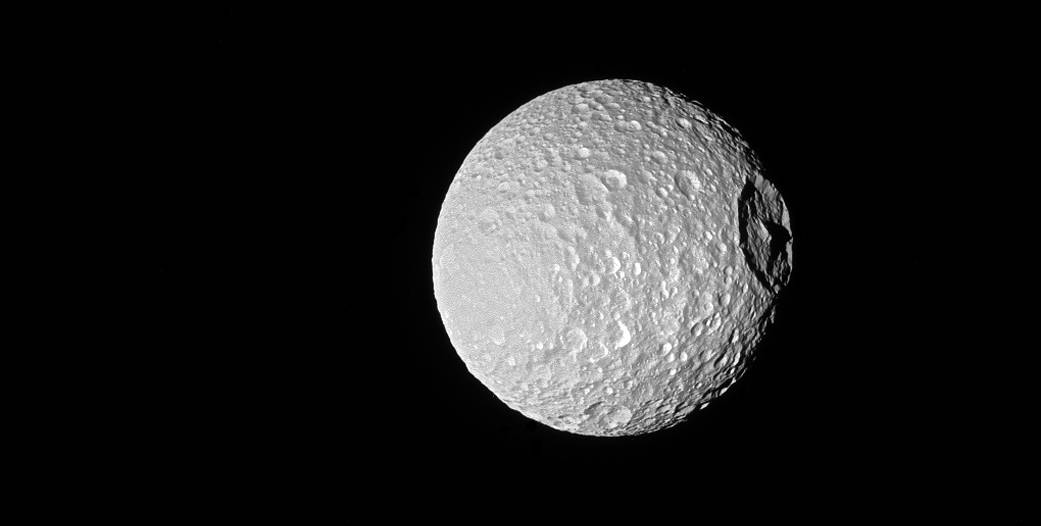
Shadows cast across Mimas’ defining feature, Herschel Crater, provide an indication of the size of the crater’s towering walls and central peak.
Named after the icy moon’s discoverer, astronomer William Herschel, the crater stretches 86 miles (139 kilometers) wide — almost one-third of the diameter of Mimas (246 miles or 396 kilometers) itself.
Large impact craters often have peaks in their center — see Tethys’ large crater Odysseus in PIA08400. Herschel’s peak stands nearly as tall as Mount Everest on Earth.
This view looks toward the anti-Saturn hemisphere of Mimas. North on Mimas is up and rotated 21 degrees to the left. The image was taken with the Cassini spacecraft narrow-angle camera on Oct. 22, 2016 using a combination of spectral filters which preferentially admits wavelengths of ultraviolet light centered at 338 nanometers.
The view was acquired at a distance of approximately 115,000 miles (185,000 kilometers) from Mimas and at a Sun-Mimas-spacecraft, or phase, angle of 20 degrees. Image scale is 3,300 feet (1 kilometer) per pixel.
The Cassini mission is a cooperative project of NASA, ESA (the European Space Agency) and the Italian Space Agency. The Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, manages the mission for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate, Washington. The Cassini orbiter and its two onboard cameras were designed, developed and assembled at JPL. The imaging operations center is based at the Space Science Institute in Boulder, Colorado.
For more information about the Cassini-Huygens mission visit http://saturn.jpl.nasa.gov and https://www.nasa.gov/cassini. The Cassini imaging team homepage is at http://ciclops.org.
Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Space Science Institute