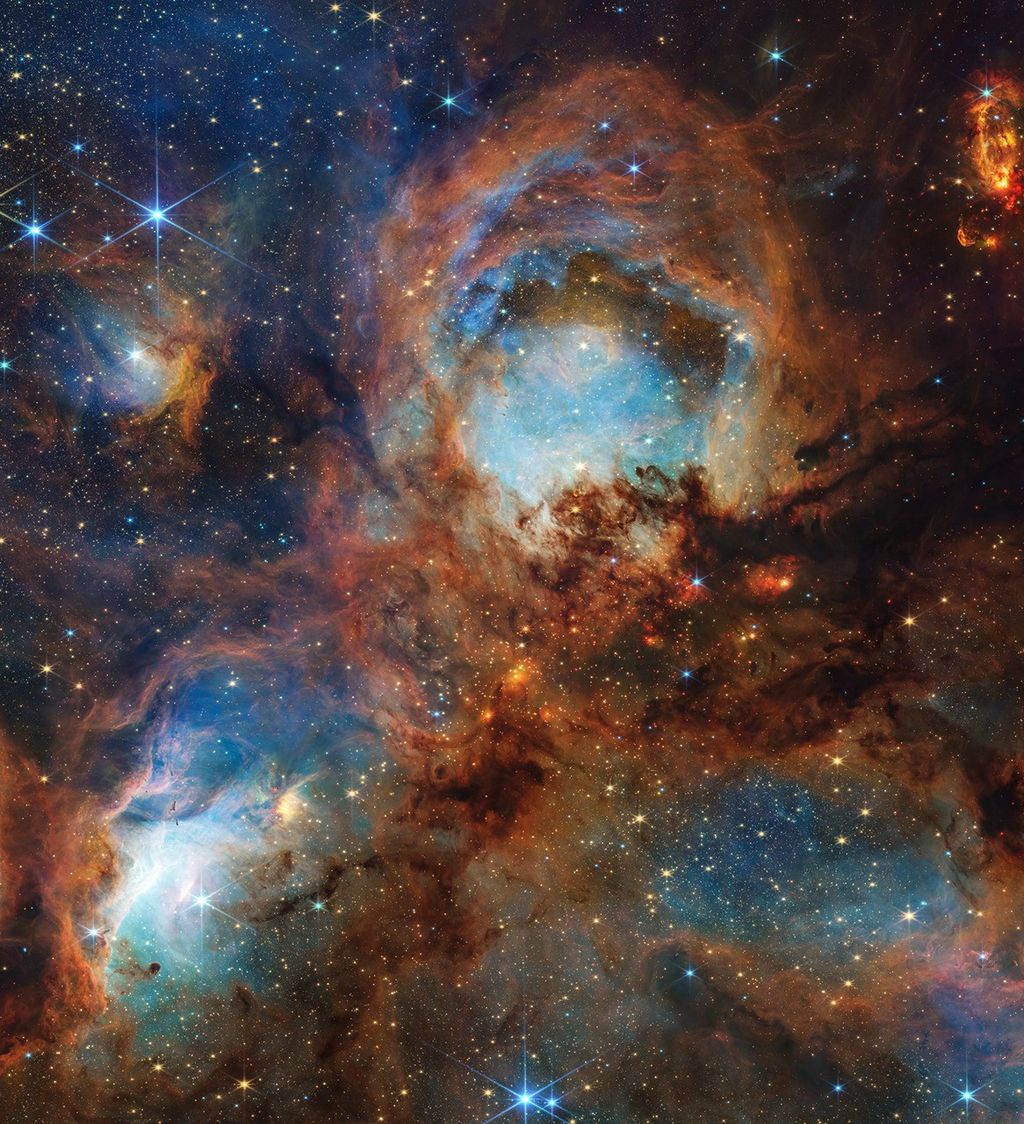
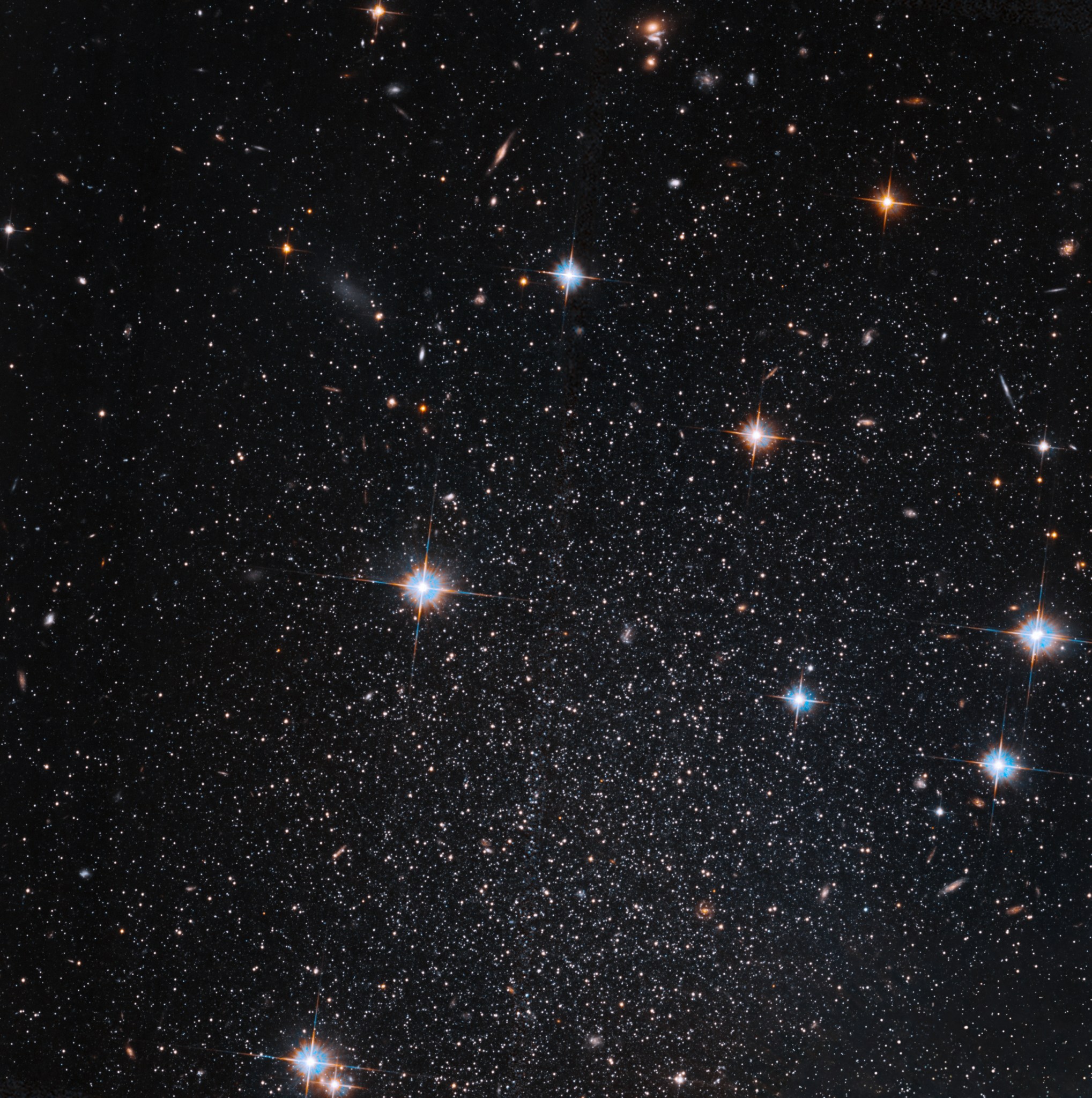
A glittering collection of stars shines against a background of much more distant galaxies in this view from NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope of the Pegasus Dwarf spheroidal galaxy, also known as Andromeda VI.
The Andromeda galaxy, also known as Messier 31, is the Milky Way’s closest grand spiral galaxy neighbor, and is host to at least 13 dwarf galaxies that orbit around it. The Pegasus Dwarf spheroidal galaxy is one of these mini-galaxies. Dwarf spheroidal galaxies are the dimmest and least massive galaxies known. They tend to have elliptical shapes and relatively smooth distributions of stars. Dwarf spheroidal galaxies are usually devoid of gas and dominated by old and intermediate-age stars, although some have experienced small amounts of recent star formation.
The Pegasus Dwarf Spheroidal galaxy was discovered in 1998 and has been characterized as having a small amount of heavy elements and little of the gas needed to form another generation of stars ― though more than many of the dwarf spheroidal galaxies within our Local Group of galaxies. Researchers suspect that Andromeda’s gravitational field may have stripped the star-forming gases from it, leaving a dearth of material to build more than a few generations of stars. In comparison, some of the dwarf spheroidal companion galaxies of the Milky Way found at comparable distances do contain some intermediate-age stars, but this could be because Andromeda is so massive and extended that its gravitational effects extend farther.
The jury is still out on how dwarf spheroidal galaxies form. Theories include collisions between galaxies that break off small fragments, the gravitational influence of larger galaxies on small disk-shaped dwarf galaxies, and processes associated with the birth of small systems among collections of dark matter. Andromeda and the Milky Way are the only galaxies close enough for astronomers to view these dim satellite galaxies, so clues to their formation will have to come from close neighbors like this one.
Hubble studied this galaxy as part of an examination of the entire Andromeda system of satellites in order to investigate such critical matters as dark matter, reionization, and the growth of galactic ecosystems across cosmic time.
Media Contact:
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov