Nothing gets a geologist more excited than layered bedrock, except perhaps finding a fossil or holding a meteorite in your hand. All of these things create a profound feeling of history, the sense of a story that took place ages ago, long before we came appeared. Layered bedrock in particular tells a story that was set out chapter by chapter as each new layer was deposited on top of older, previously deposited layers.
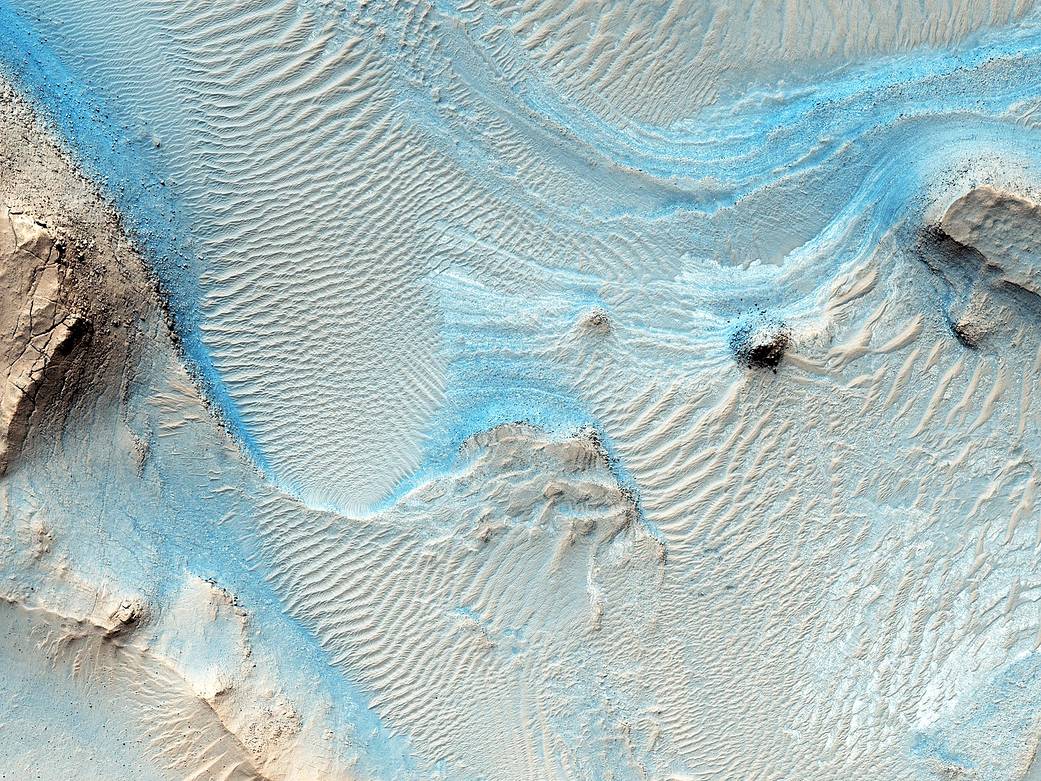
Here in Nili Fossae, we see layered bedrock as horizontal striations in the light toned sediments in the floor of a canyon near Syrtis Major. (Note: illumination is from the top of the picture) The ancient layered rocks appear in pale whitish and bluish tones. They are partially covered by much younger ripples made up of dust and other wind blown sediments. The rock of the nearby canyon wall is severely fractured and appears to have shed sand and rocks and boulders onto the floor. This canyon did not form by fluvial erosion: it is part of a system of faults that formed a series of graben like this one, but water probably flowed through Nili Fossae in the distant past.
Orbital spectral measurements by the OMEGA instrument on Mars Express and CRISM on MRO detected an abundance of clay minerals of different types in the layered sediments inside Nili Fossae, along with other minerals that are typical of sediments that were deposited by water. The various colors and tones of the layered rocks record changes in the composition of the sediments, details that can tell us about changes in the Martian environment eons ago. Nili Fossae is a candidate site for a future landed robotic mission that could traverse across these layers and make measurements that could be used to unravel a part of the early history of Mars. Nili Fossae is a history book that is waiting to be read.
The University of Arizona, Tucson, operates HiRISE, which was built by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp., Boulder, Colo. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, manages the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter Project for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate, Washington.
Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Univ. of Arizona