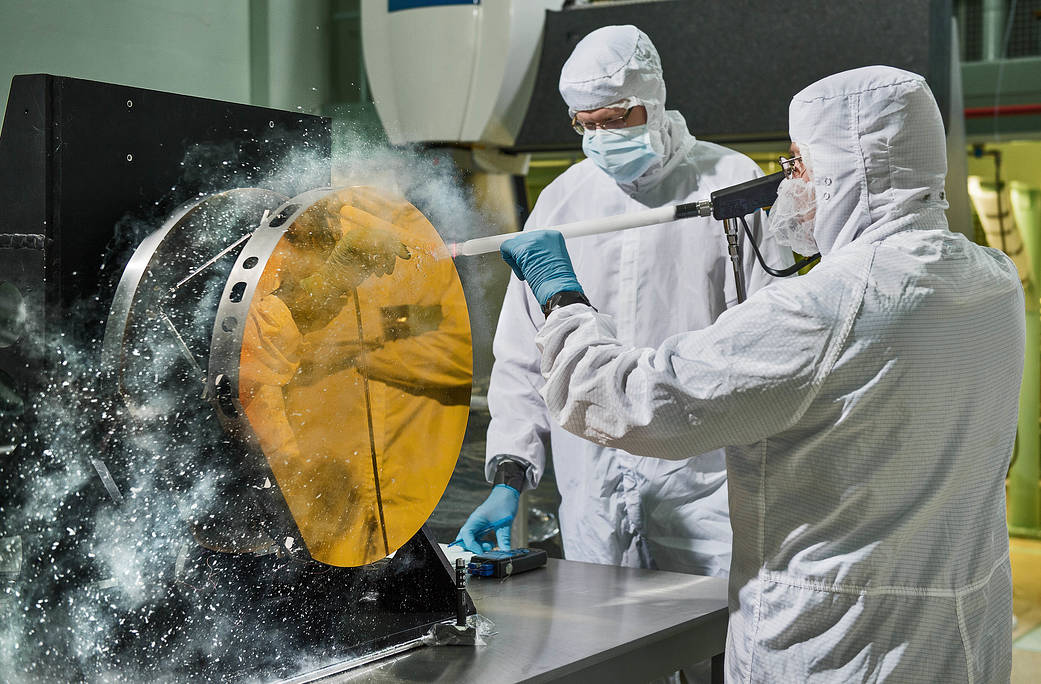
Just like drivers sometimes use snow to clean their car mirrors in winter, two Exelis Inc. engineers are practicing “snow cleaning'” on a test telescope mirror for the James Webb Space Telescope at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. By shooting carbon dioxide snow at the surface, engineers are able to clean large telescope mirrors without scratching them.
“The snow-like crystals (carbon dioxide snow) knock contaminate particulates and molecules off the mirror,” said Lee Feinberg, NASA optical telescope element manager. This technique will only be used if the James Webb Space Telescope’s mirror is contaminated during integration and testing.
The Webb telescope is the scientific successor to NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope. It will be the most powerful space telescope ever built. With a mirror seven times as large as Hubble’s and infrared capability, Webb will be capturing light from 13.5 billion light years away. To do this, its mirror must be kept super clean.
“Small dust particles or molecules can impact the science that can be done with the Webb,” said Feinberg. “So cleanliness especially on the mirrors is critical.”
Webb is an international project led by NASA with its partners, the European Space Agency and the Canadian Space Agency.
Image credit: NASA/Chris Gunn
Text credit: Laura Betz, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Maryland