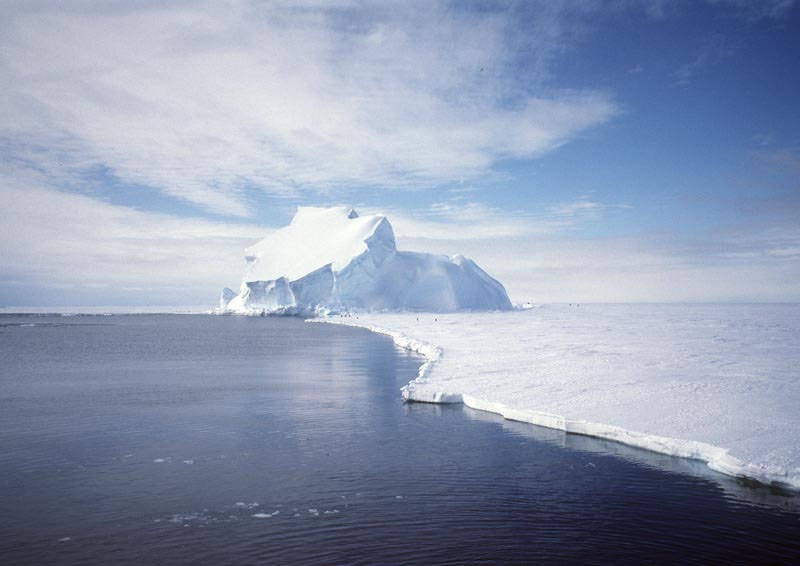
For millions of years, Antarctica, the frozen continent at the southern end of the planet, has been encased in a gigantic sheet of ice. Recently, the Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) satellite has been taking sensitive measurements of the gravity for the entire Earth, including Antarctica. Recent analysis of GRACE data indicate that the Antarctic ice sheet might have lost enough mass to cause the worlds’ oceans to rise about .05 inches, on the average, from between 2002 and 2005.
Although this may not seem like much, the equivalent amount of water is about 40 trillion gallons, equivalent to the amount of water used by U.S. residents in three months. Uncertainties in the measurement make the mass loss uncertain by about 21 trillion gallons. The iceberg pictured above is a small part of the Antarctic ice sheet. The picture was taken on the Riiser-Larsen ice shelf in December 1995. Future research will likely focus on trying to better understand the data, take more data, predict future trends, and understand possible effects of these trends on the future climate of our entire home planet.Image credit: NASA/GRACE team/DLR/Ben Holt Sr.