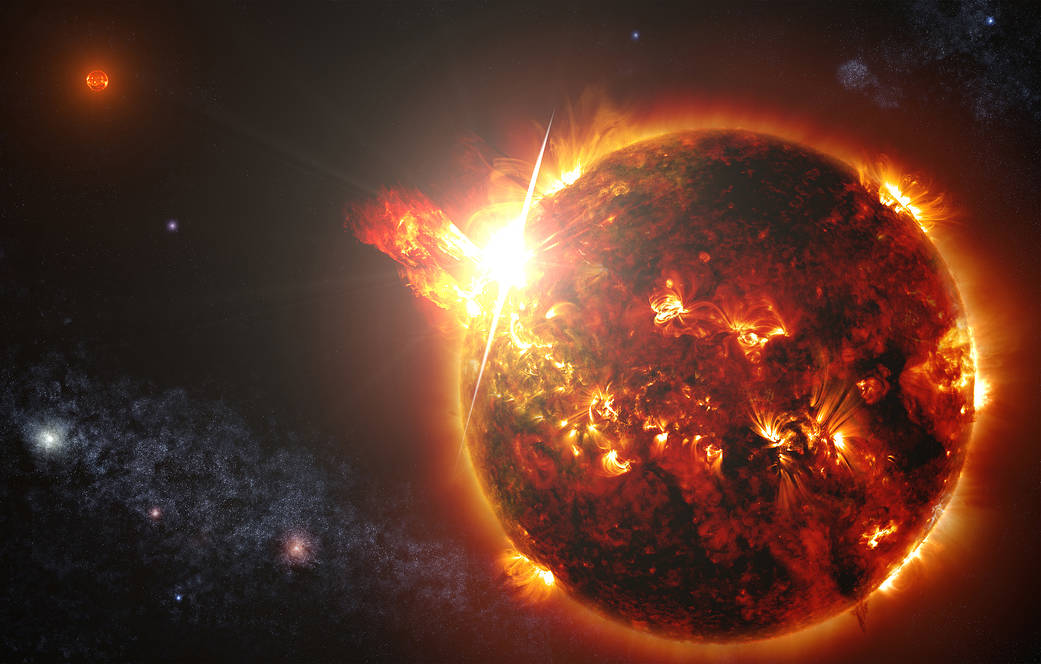
This artist’s illustration depicts a coronal mass ejection, or CME, which involves a large-scale expulsion of material, and have frequently been observed on our Sun. A new study using the Chandra X-ray Observatory detected a CME from a star other than our own for the first time, providing a novel insight into these powerful phenomena. As the name implies these events occur in the corona, which is the outer atmosphere of a star.
This “extrasolar” CME was seen emanating from a star called HR 9024, which is located about 450 light years from Earth. This represents the first time that researchers have thoroughly identified and characterized a CME from a star other than our Sun. This event was marked by an intense flash of X-rays followed by the emission of a giant bubble of plasma, i.e., hot gas containing charged particles.
Image Credit: NNASA/CXC/INAF/Argiroffi, C. et al./S. Wiessinger