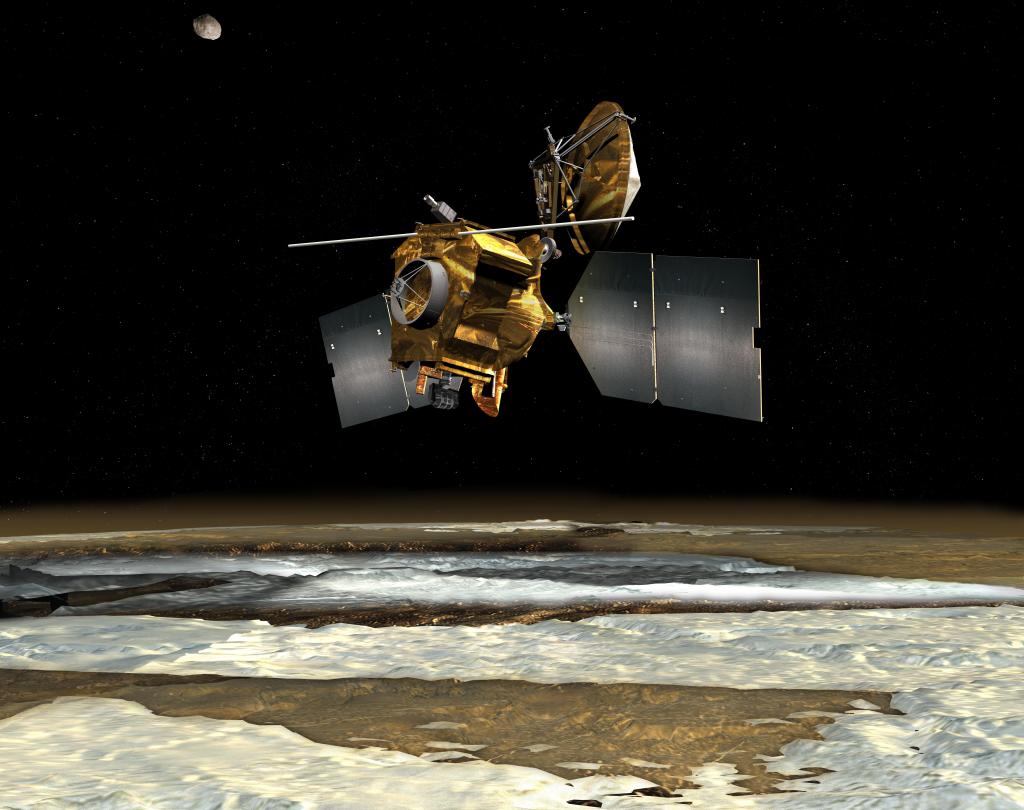
After the success of Pioneers 10 and 11, NASA’s Ames Research Center in California’s Silicon Valley turned their focus on Venus, Earth’s closest cousin for their next mission in the Pioneer series. Launched 40 years ago on May 20, 1978, aboard an Atlas-Centaur launch vehicle from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the Pioneer Venus Orbiter is also known as Pioneer 12 or Pioneer Venus 1. The Pioneer Venus Orbiter carried 17 experiments and investigated the atmosphere of Venus as part of an orbiter-probe combination.
Insertion into Venus’ atmosphere occurred December 4, 1978. The Pioneer Venus Orbiter measured data from the upper atmosphere and southern region of the planet, including interactions between solar winds and Venus’ magnetic field. It also mapped Venus’ surface. The spacecraft confirmed an atmosphere with clouds, mainly of sulfuric acid, with little magnetic field. Additional topography studies found the planet to be generally smoother than the surface of Earth, but Venus has a mountain higher than Mount Everest’s peaks and a chasm deeper than the Grand Canyon. With its fuel reserves exhausted, after spending 14 years conducting research, Pioneer Venus Orbiter plunged through Venus’ atmosphere, burning up as it did so on October 8, 1992.
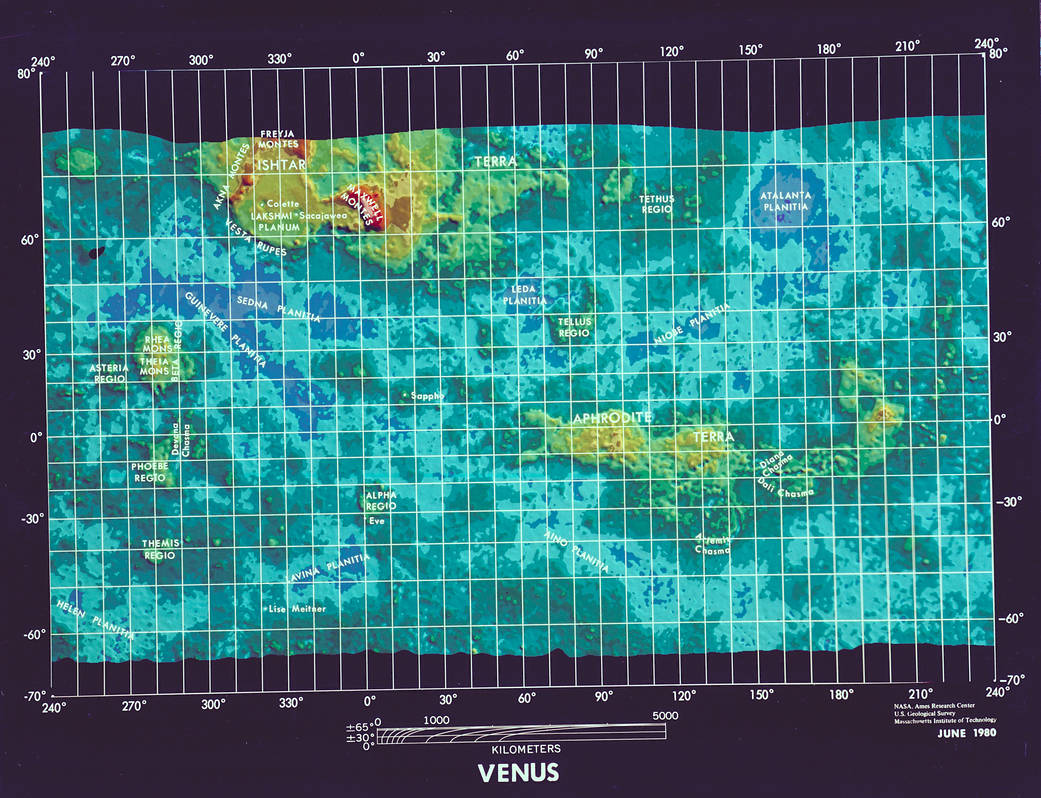
Map of Venus compiled from data recorded by Pioneer Venus Orbiter spacecraft. Image credit: NASA/Ames/U.S. Geological Survey/Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Check out a related story from NASA’s Johnson Space Center: 40 years ago, Pioneer Venus Orbiter launched