Overview
Using the engineering design process, students will design and build a model of a spacecraft that can safely transport two astronauts on a mission to the Moon, Mars, or other destinations in space. A drop test will determine how well the spacecraft will protect the astronauts during landing. During the drop test, the model spacecraft will be deployed, or dropped, from a height of at least two meters to simulate landing. The astronauts must stay securely in their seats during the drop test. The spacecraft must also have an internal tank for fuel.
Supporting Science Investigations:
- Egg Drop Challenge – Discover how to protect a falling object using readily available classroom materials.
- Wall Smashers – See the effects of drag on a moving object by controlling the speed of a ball hitting a wall.
Introduction Video
Challenge Content
EDC-04: Spacecraft Safety – Facilitation Guide (coming soon)
EDC-04: Spacecraft Safety – Facilitator Presentation
Next Generation Science Standards Addressed
Engineering Design
- MS–ETS1-1. Define the criteria and constraints of a design problem with sufficient precision to ensure a successful solution, taking into account relevant scientific principles and potential impacts on people and the natural environment that may limit possible solutions.
- MS–ETS1–2. Evaluate competing design solutions using a systematic process to determine how well they meet the criteria and constraints of the problem.
- MS–ETS1–3. Analyze data from tests to determine similarities and differences among several design solutions to identify the best characteristics of each that can be combined into a new solution to better meet the criteria for success.
- MS–ETS1–4. Develop a model to generate data for iterative testing and modification of a proposed object, tool, or process such that an optimal design can be achieved.
Forces and Interactions
- MS–PS2–1. Apply Newton’s Third Law to design a solution to a problem involving the motion of two colliding objects.
Related NASA Content
Online Resources
- NASA’s Orion Spacecraft – Learn about NASA’s new spacecraft that will take astronauts to the Moon, Mars, or other destinations in space.
http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/systems/orion - NASA’s Space Launch System – Discover NASA’s new rocket system that will launch Orion.
http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/systems/sls - The Voyager Program – Explore a historic mission through the solar system that is still going strong over 40 years later!
http://voyager.jpl.nasa.gov/ - New Horizons – Learn more about the New Horizons spacecraft and its exploration of Pluto and the outer solar system.
https://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/newhorizons/main/index.html - Moon to Mars Plans – Visit the Moon to Mars homepage to learn about NASA’s efforts to accomplish its goal of sending humans back to the moon and on to the Red Planet.
https://www.nasa.gov/topics/moon-to-mars
Informational Videos
- Orion: Trial By Fire – Find out about Orion’s development and the details of Exploration Flight Test-1.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KyZqSWWKmHQ - Orion Backstage: Chris Cassidy and Heather Paul – Hear from two astronauts about how the inside of Orion is configured to support a crew.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Gm8ECUMYBFg - Orion Swing Drop at NASA Langley Research Center – Watch as a test version of the Orion spacecraft is taken through a splashdown test at the Hydro Impact Basin.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8sR2jKIzef4 - Orion Backstage: Up the Hatch with Astronauts – Look on as engineers and astronauts gather feedback on the design of Orion’s docking hatch.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=X-I0katihQo
Contact Information
Gerald Voltz
Education Program Specialist
gerald.w.voltz@nasa.gov
(216) 433-8817
Glenn Research Center – Office of STEM Engagement
Phone: (216) 433-6656
Email: GRC-Ed-Opportunities@nasa.gov
Latest Content
Stay up-to-date with the latest content from NASA as we explore the universe and discover more about our home planet.

Written by Abigail Fraeman, Deputy Project Scientist at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory Earth planning date: Thursday, July 3, 2025 The…

Written by Lucy Thompson, APXS Collaborator and Senior Research Scientist at the University of New Brunswick, CanadaEarth planning date: Wednesday,…
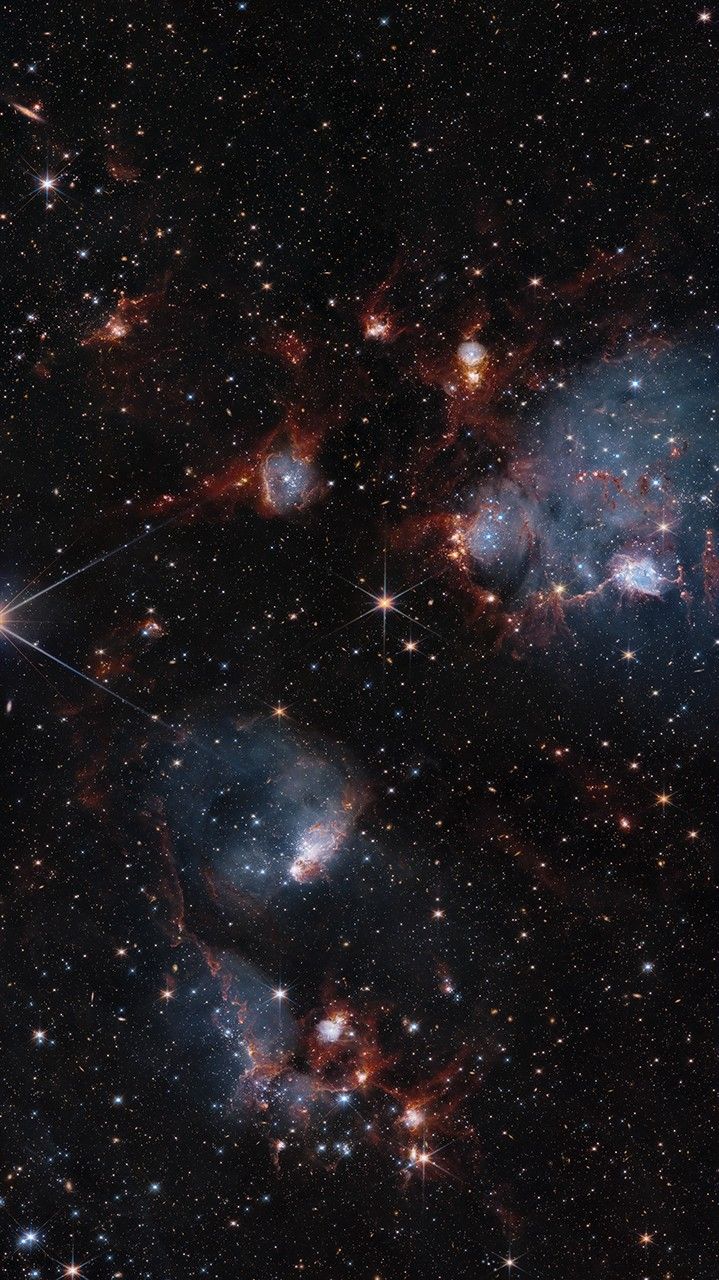

A riotous expanse of gas, dust, and stars stake out the dazzling territory of a duo of star clusters in…