ECN-2059
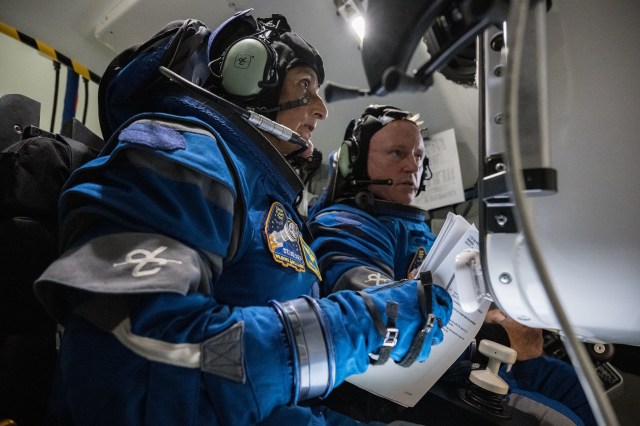
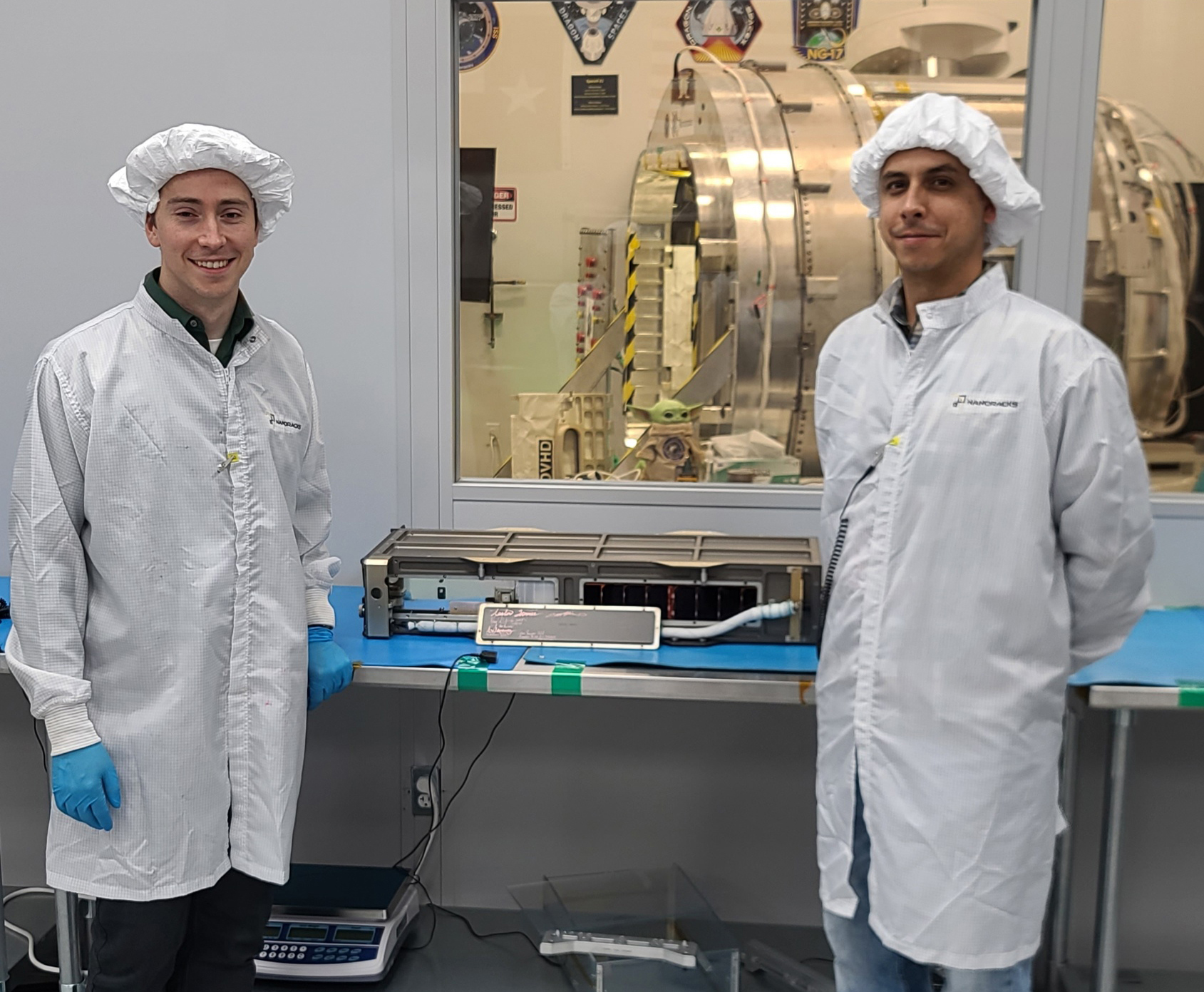
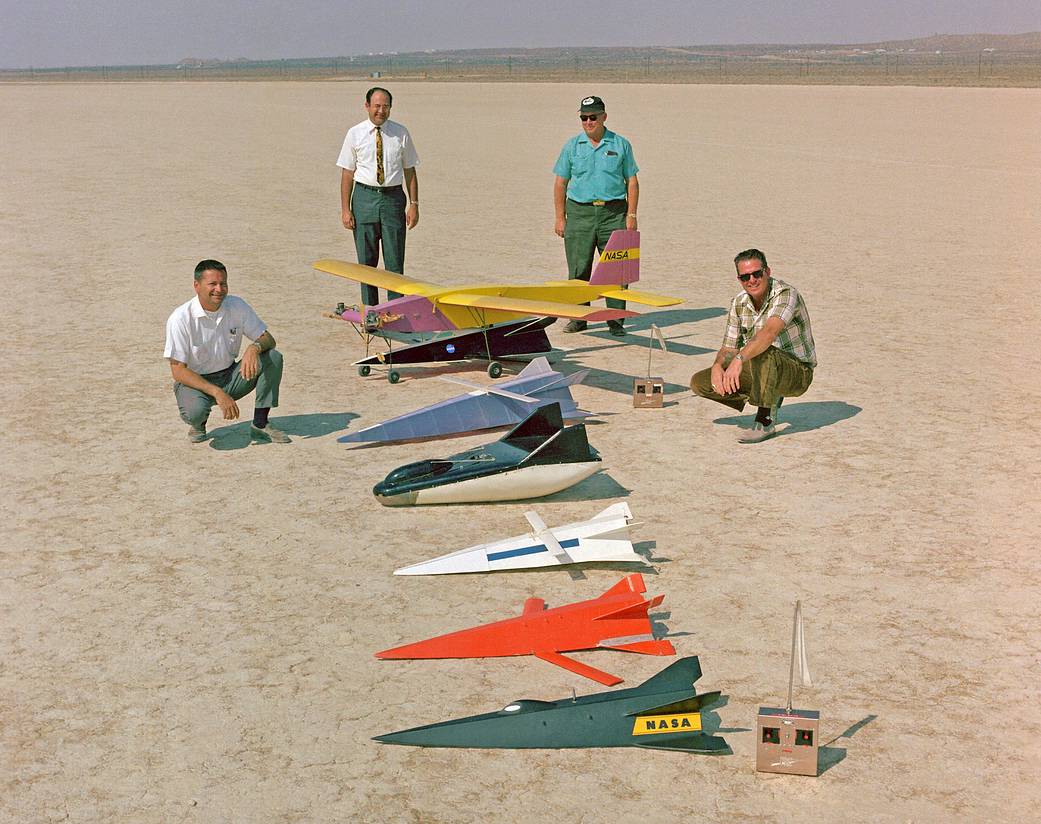
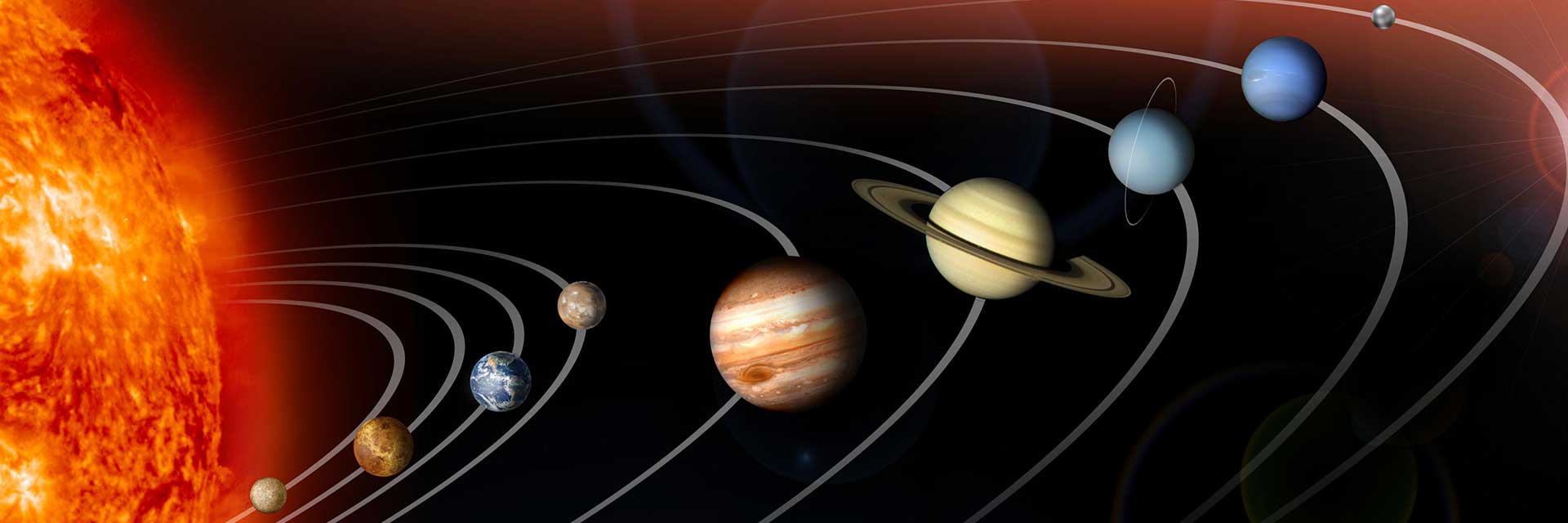
Richard C. Eldredge, Dale Reed, James O. Newman, and Bob McDonald with the mothership (top) and other models. Over the years, the Dryden Flight Research Center and its predecessors have flown various models to gather data for various purposes. The mothership has been used to launch the models.
The Flight Research Center (FRC – as Dryden was named from 1959 until 1976) already had experience with testing small-scale aircraft using model-airplane techniques, but the first true remotely piloted research vehicle was the full-sized Hyper III, which flew only once in December 1969. At that time, the Center was engaged in flight research with a variety of reentry shapes called lifting bodies, and there was a desire both to expand the flight research experience with maneuverable reentry vehicles, including a high-performance, variable-geometry craft, and to investigate a remotely piloted flight research technique that made maximum use of a research pilot’s skill and experience by placing him “in the loop” as if he were in the cockpit.
The Hyper III as originally conceived was a stiletto-shaped lifting body that had resulted from a study at NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, VA. It was one of a number of hypersonic, cross-range reentry vehicles studied at Langley. (Hypersonic means Mach 5-five times the speed of sound-or faster; cross-range means able to fly a considerable distance to the left or right of the initial reentry path.) The FRC added a small, deployable, skewed wing to compensate for the shape’s extremely low glide ratio. Shop personnel built the 32-foot-long Hyper III and covered its tubular frame with dacron, aluminum, and fiberglass, for about $6,500.
Hyper III employed the same “8-ball” attitude indicator developed for control-room use when flying the X-15, two model-airplane receivers to command the vehicle’s hydraulic controls, and a telemetry system (surplus from the X-15 program) to transmit 12 channels of data to the ground not only for display and control but for data analysis. Dropped from a helicopter at 10,000 feet, Hyper III flew under the control of research pilot Milt Thompson to a near landing using instruments for control. When the vehicle was close to the ground, he handed the vehicle off to experienced model pilot Dick Fischer for a visual landing using standard controls. The flight demonstrated the feasibility of remotely piloting research vehicles and, among other things, that control of the vehicle in roll was much better than predicted and that the vehicle had a much lower lift-to-drag ratio than predicted (a maximum of 4.0 rather than 5.0).
Pilot Milt Thompson exhibited some surprising reactions during the Hyper III flight; he behaved as if he were in the cockpit of an actual research aircraft.June 26, 1968
NASA Photo
3 min read