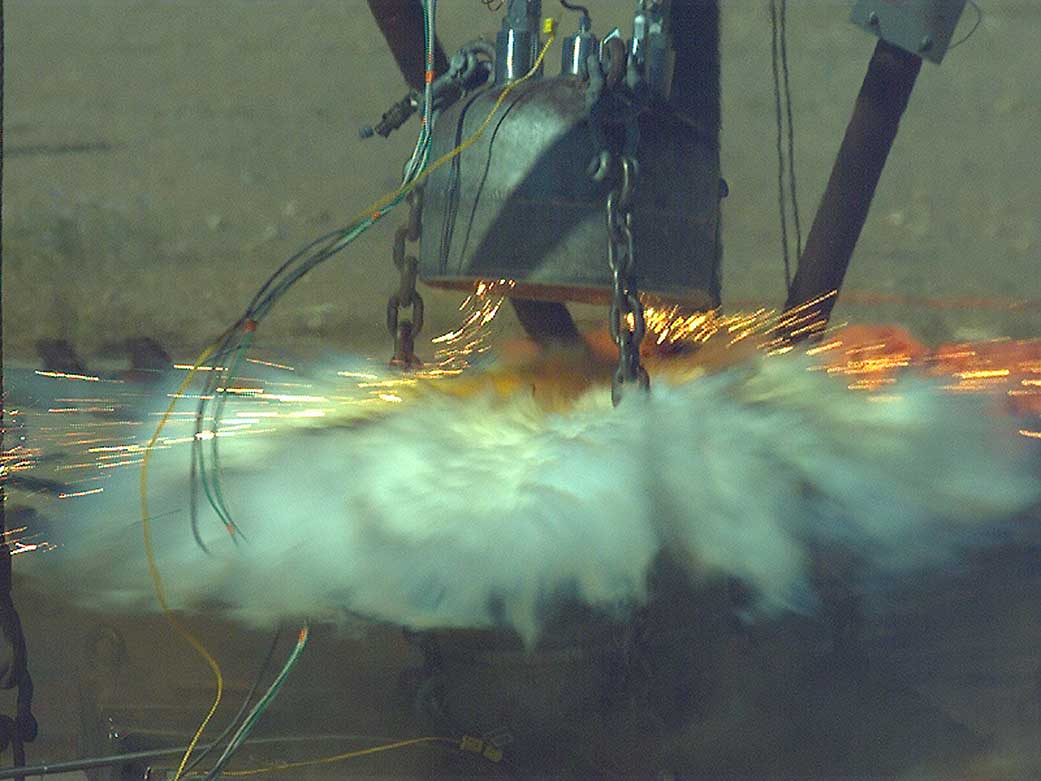
White Sands Test Facility performs testing to understand the hazards associated with energetic materials such as aerospace propellants. These materials are very reactive and there are hazards associated with stability, thermal runaway, and flammability.
Stability
Stability of propellants is a concern for spacecraft propulsion systems and storage facilities. We perform testing to determine the stability and materials interactions of aerospace propellants in contact with materials of construction, contaminants, or stabilizing additives.
Catalytic decomposition of a propellant in contact with a surface, decomposition catalyzed by a contaminant, or autocatalytic decomposition when the chemical itself is the catalyst for a reaction are some of the reactions that can be studied.
Thermal Runaway
Thermal runaway refers to a situation where an increase in temperature changes the conditions in a way that causes a further increase in temperature, often leading to an explosion. White Sands can determine the kinetic parameters of the reactions allowing the prediction of hazardous situations.
Flammability
Assessing ignition hazards relies on important parameters such as flash point and minimum ignition energy (MIE). We conduct ignition and flammability testing following NASA and American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) test methods for determining the flammability limits for fuels as a function of concentration, temperature, pressure, and partial pressures of oxygen.