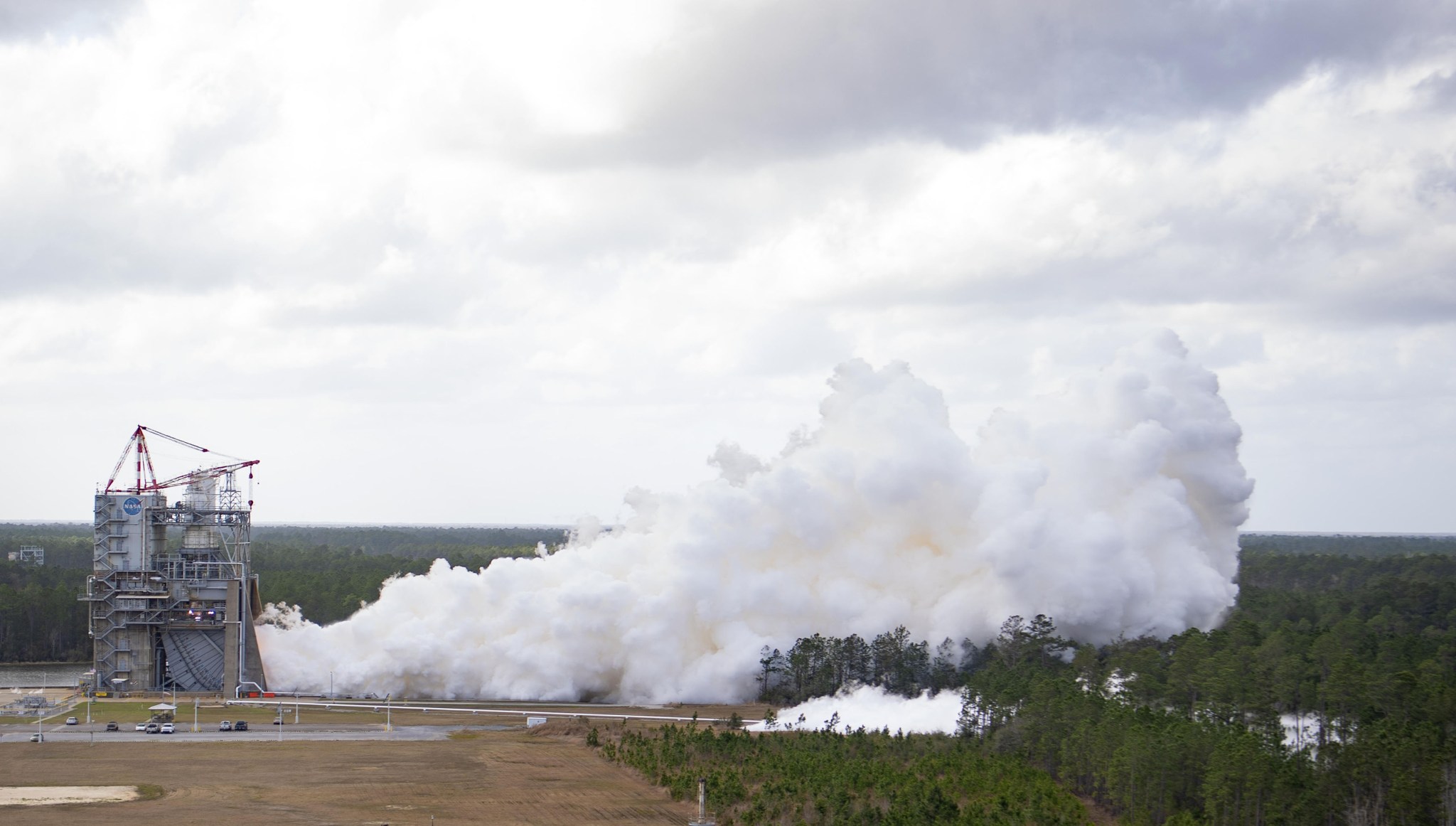
Engineers hot fire test a redesigned RS-25 engine Feb. 22 for future flights of the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket on Artemis missions to the Moon. The test, conducted on the Fred Haise Test Stand at NASA’s Stennis Space Center, is part of a certification series to support production of new RS-25 engines by lead SLS engines contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne.
As NASA explores the secrets of the universe for the benefit of all, the new engines will help power future Artemis missions, beginning with Artemis V. Operators fired the RS-25 engine up to 111% power level – the same level needed to help the SLS lift the Orion spacecraft and other future payloads to orbit – for 10 minutes (600 seconds), more than the 500 seconds the engines must operate to reach space. Longer-duration hot fires allow operators to test the limits of engine performance and provide a margin of safety for flight operations.
The hot fire is the latest in an ongoing series of tests to certify new manufacturing techniques and processes for production of RS-25 engines. Four engines fire simultaneously, providing up to 2 million pounds of combined thrust, to help power the launch of the SLS to orbit.