The newest satellite to monitor global sea level is ready for its journey into space. Here’s what to expect.
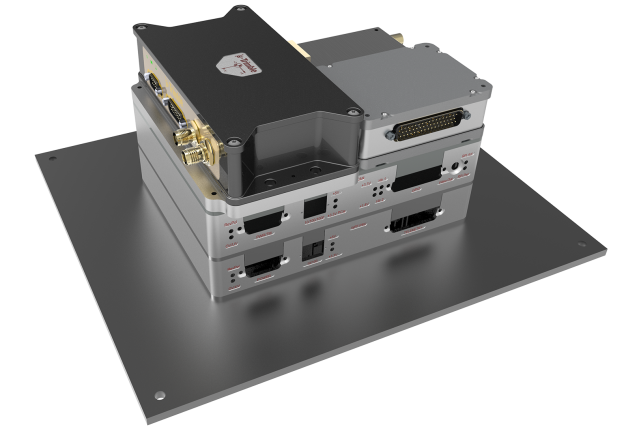
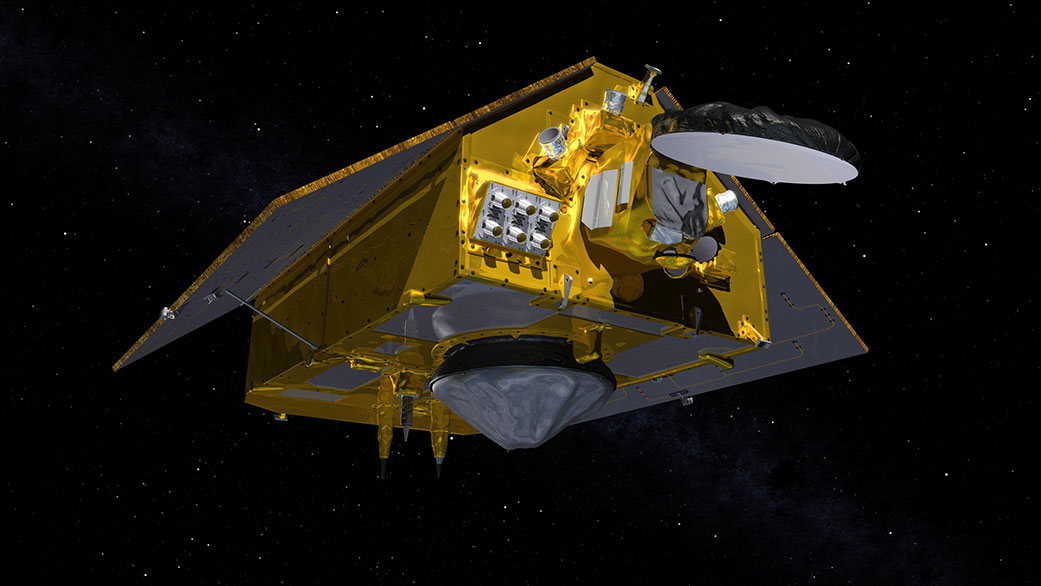
Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich, the latest in a series of spacecraft designed to monitor our oceans, is scheduled to launch from Vandenberg Air Force Base in central California on Saturday, Nov. 21, 2020. The satellite will be followed in 2025 by its twin, Sentinel-6B. Together, the pair is tasked with extending our nearly 30-year-long record of global sea surface height measurements. Instruments aboard the satellites will also provide atmospheric data that will improve weather forecasts, climate models, and hurricane tracking.
Launch Timeline
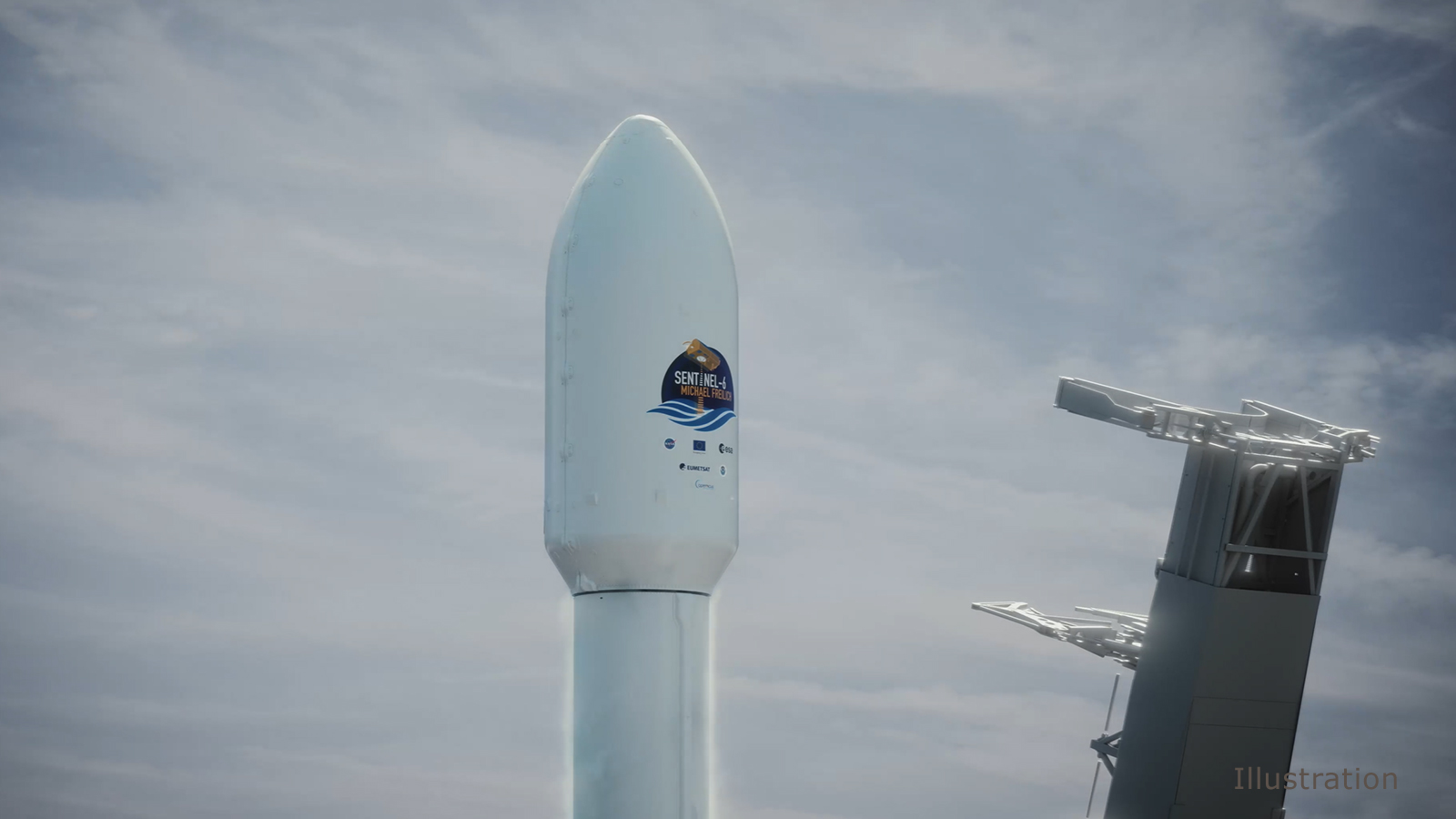
Named after former NASA Earth Science Division Director Michael Freilich, the U.S.-European satellite will be carried into space on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, with liftoff targeted for 9:17:08 a.m. PST (12:17:08 p.m. EST) from Space Launch Complex 4 East. If needed, backup launch opportunities are available on subsequent days, with the instantaneous launch window falling about 12 minutes earlier each day.
A little more than two minutes after the Falcon 9 rocket lifts off, the main engine will cut off. Shortly after, the rocket’s first and second stages will separate, followed by second-stage engine start. The reusable Falcon 9 first stage will then begin its automated boost-back burn to the launch site for a propulsive landing.
The first cutoff of the second stage engine will take place approximately eight minutes after liftoff. It will fire a second time 45 minutes later, at which point the launch vehicle and the spacecraft will be in a temporary “parking” orbit. Several minutes later, the launch vehicle and the spacecraft will separate. The satellite will begin solar panel deployment about one hour and seven minutes post-launch and is expected to make first contact about 25 minutes after that.
More About the Mission
Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich and Sentinel-6B make up the Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission, which was developed by ESA (European Space Agency) in the context of the European Copernicus program led by the European Commission, the European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites (EUMETSAT), NASA, and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), with funding support from the European Commission and technical support from France’s National Centre for Space Studies (CNES).
JPL, a division of Caltech in Pasadena, built three science instruments for each Sentinel-6 satellite: the Advanced Microwave Radiometer, the Global Navigation Satellite System – Radio Occultation, and the Laser Retroreflector Array. NASA is also contributing launch services, ground systems supporting operation of the NASA science instruments, the science data processors for two of these instruments, and support for the international Ocean Surface Topography Science Team. The launch is managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
Where to Find Launch Coverage
On launch day, Nov. 21, 2020, NASA TV coverage will begin at 8:45 a.m. PST (11:45 a.m. EST).
For live NASA TV programming on NASA’s public channel, visit:
For live programming on the NASA TV media channel, visit:
NASA TV programming will be archived and available soon after it airs here:
For more information on the mission, visit:
https://sealevel.jpl.nasa.gov/missions/jason-cs-sentinel-6/summary/
Grey Hautaluoma
NASA Headquarters, Washington
202-358-0668
grey.hautaluoma-1@nasa.gov
Ian J. O’Neill / Jane J. Lee
Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif.
818-354-2649 / 818-354-0307
ian.j.oneill@jpl.nasa.gov / jane.j.lee@jpl.nasa.gov
Written by Esprit Smith, NASA’s Earth Science News team
2020-224