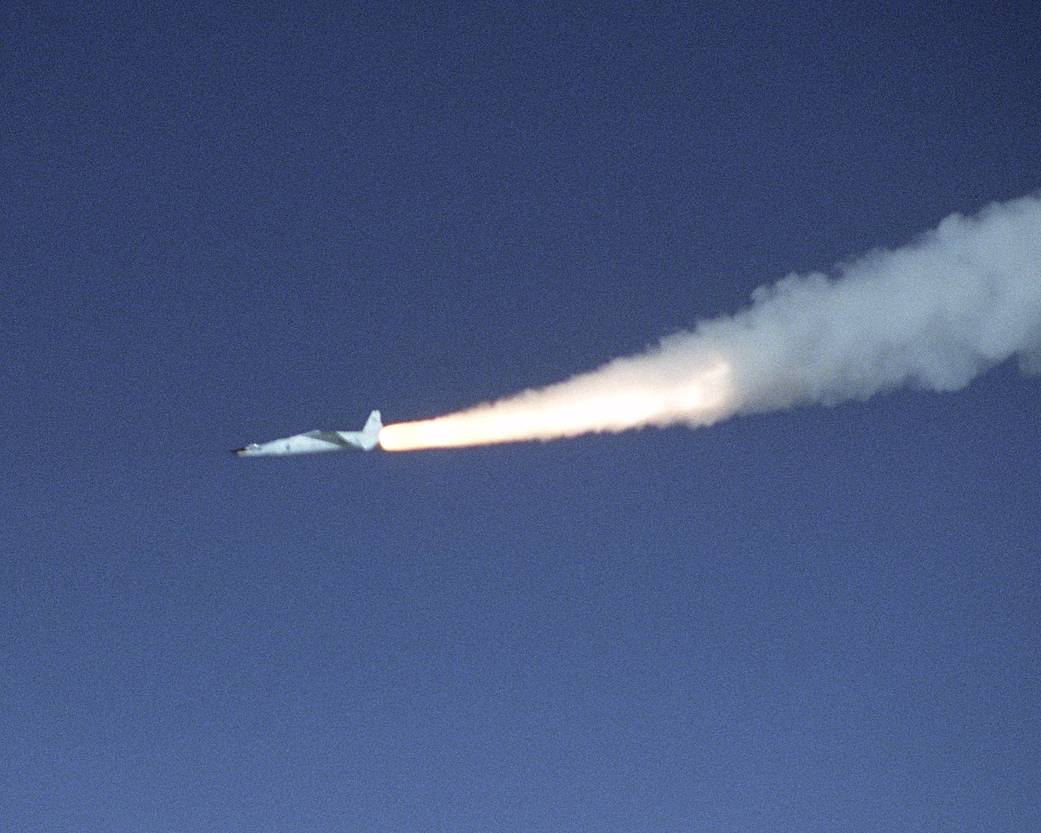
NASA’s X-43A research vehicle has screamed into the record books, demonstrating an air-breathing engine can fly at nearly 10 times the speed of sound. Preliminary data from the scramjet-powered research vehicle show its revolutionary engine worked successfully at approximately Mach 10, nearly 7000 mph, as it flew at an altitude of approximately 110,000 feet on November 16, 2004.
“This flight is a key milestone and a major step toward the future possibilities for producing boosters for sending large and critical payloads into space in a reliable, safe, inexpensive manner,” said NASA Administrator Sean O’Keefe. “These developments will also help us advance the Vision for Space Exploration, while helping to advance commercial aviation technology,” Administrator O’Keefe said.Credit: NASA+ View X-43A Main Page