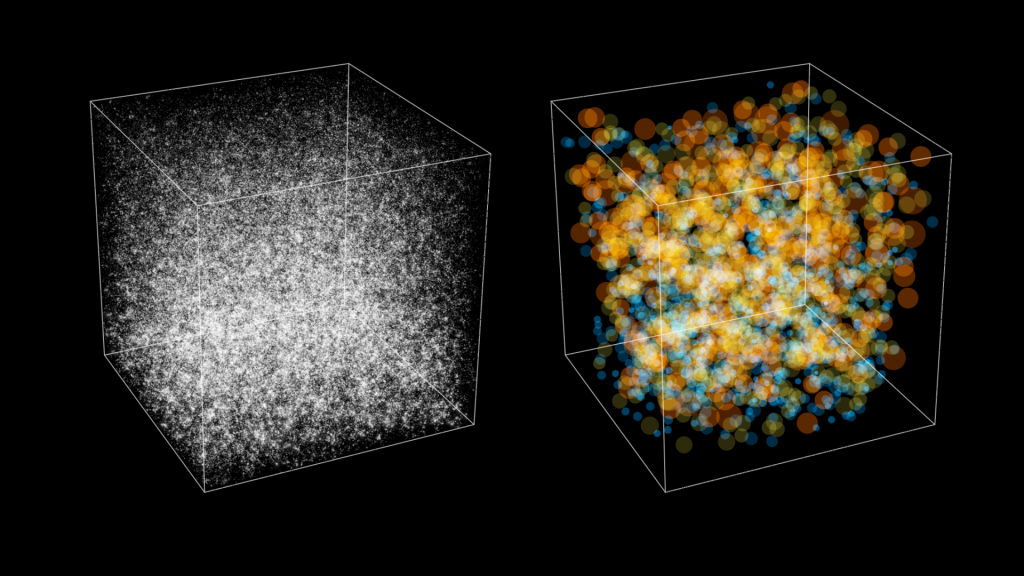
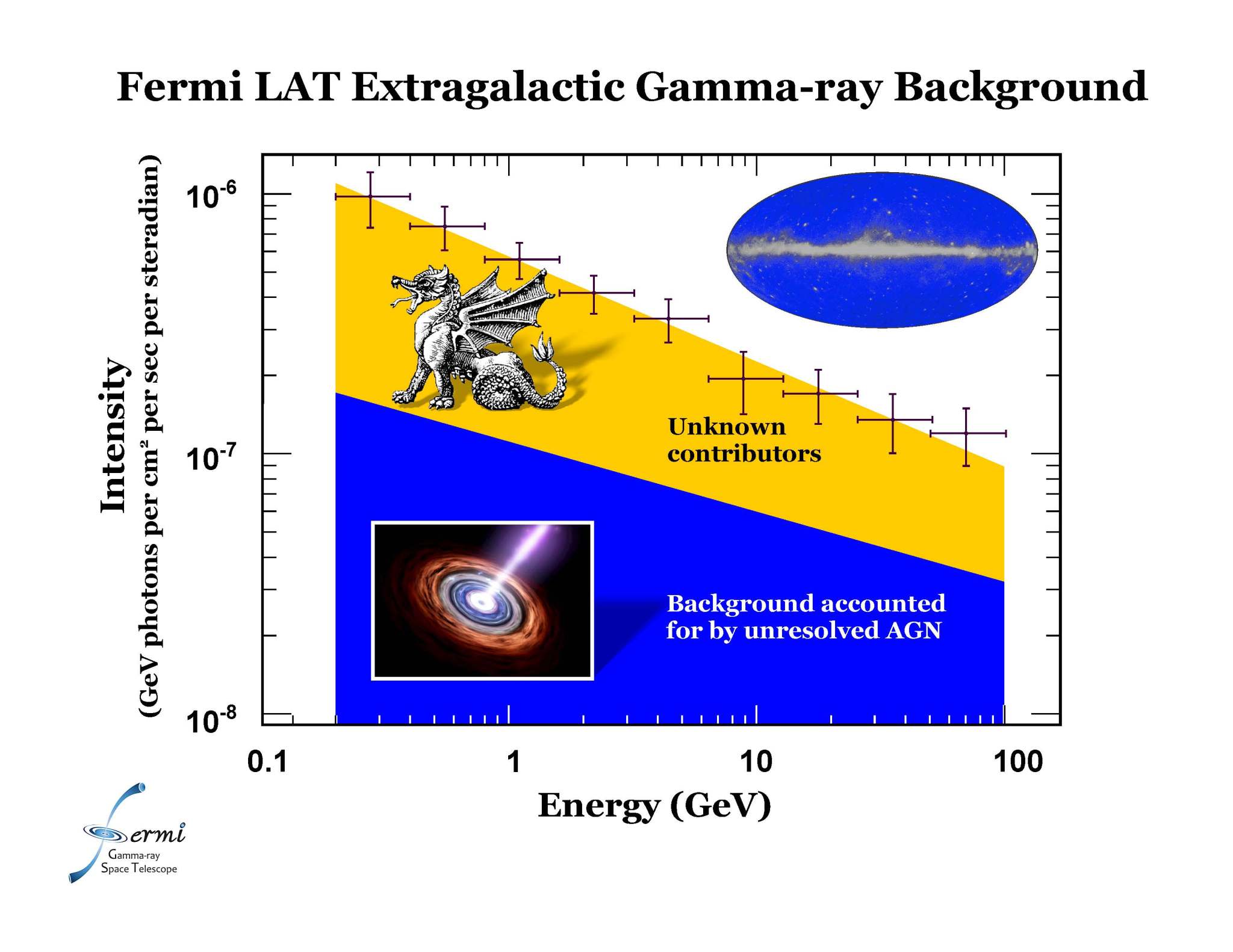
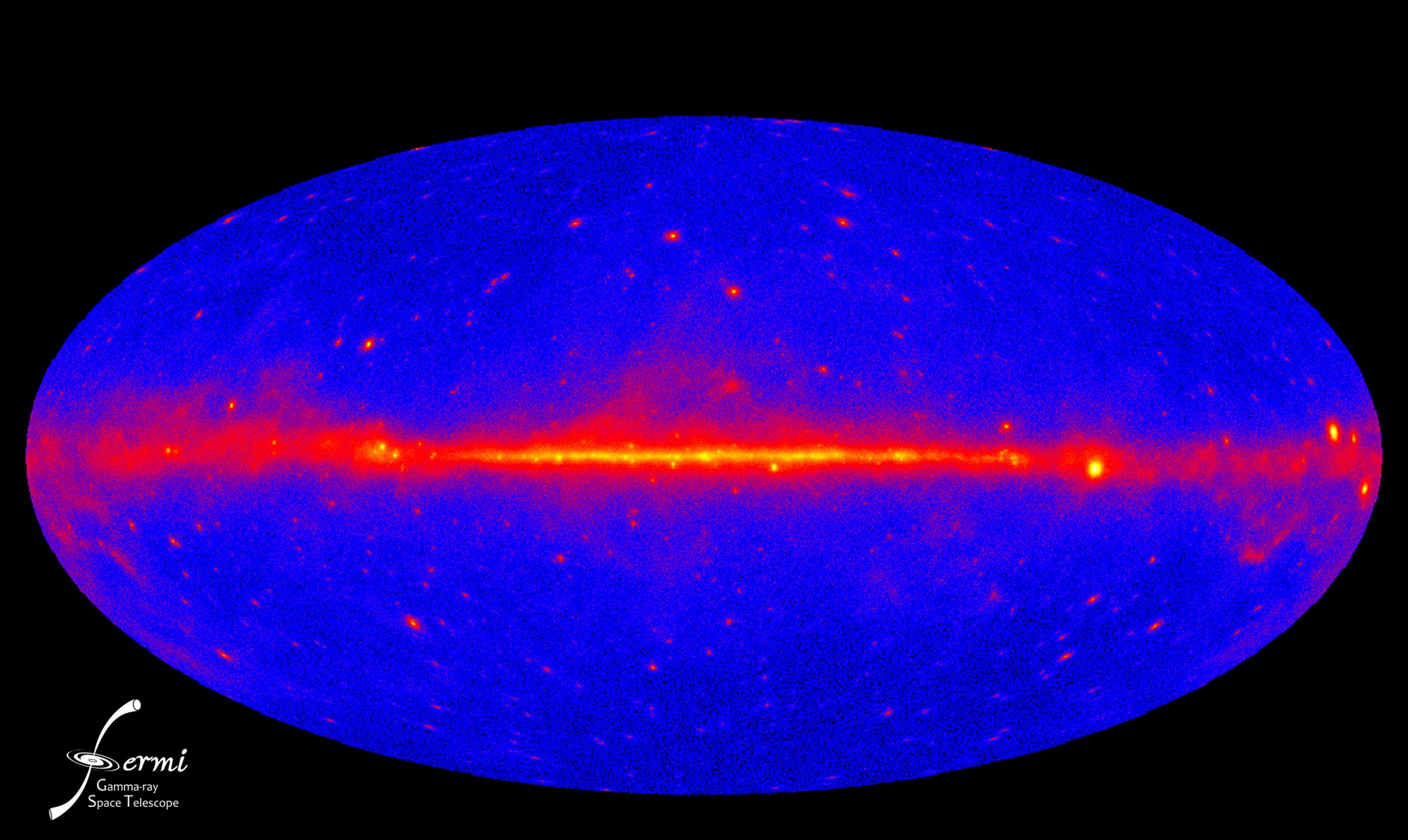
One of the pleasures of perusing ancient maps is locating regions so poorly explored that mapmakers warned of dragons and sea monsters. Now, astronomers using NASA’s Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope find themselves in the same situation as cartographers of old. A new study of the ever-present fog of gamma rays from sources outside our galaxy shows that less than a third of the emission arises from what astronomers once considered the most likely suspects – black-hole-powered jets from active galaxies.
“Active galaxies can explain less than 30 percent of the extragalactic gamma-ray background Fermi sees,” said Marco Ajello, an astrophysicist at the Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology (KIPAC), jointly located at SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory and Stanford University, Calif. “That leaves a lot of room for scientific discovery as we puzzle out what else may be responsible.”
Ajello presented his findings Tuesday at a meeting of the American Astronomical Society’s High-Energy Astrophysics Division in Waikoloa, Hawaii.
The sky glows in gamma rays even far away from bright sources, such as pulsars and gas clouds within our own Milky Way galaxy or the most luminous active galaxies. According to the conventional explanation, this background glow represents the accumulated emission of a vast number of active galaxies that are simply too faint and too distant to be resolved as discrete gamma-ray sources.
“Thanks to Fermi, we now know for certain that this is not the case,” Ajello said. A paper on the findings has been submitted to The Astrophysical Journal.
Active galaxies possess central black holes containing millions to billions of times the sun’s mass. As matter falls toward the black hole, some of it becomes redirected into jets of particles traveling near the speed of light.
These particles can produce gamma rays in two different ways. When one strikes a photon of visible or infrared light, the photon can gain energy and become a gamma ray. If one of the jet’s particles strikes the nucleus of a gas atom, the collision can briefly create a particle called a pion, which then rapidly decays into a pair of gamma rays.
Launched on June 11, 2008, the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope is continually mapping the gamma-ray sky. The mission is a partnership between astrophysics and particle physics, developed in collaboration with NASA and the U.S. Department of Energy and including important contributions from academic institutions and partners in France, Germany, Italy, Japan, Sweden, and the U.S.
The team analyzed data acquired by Fermi’s Large Area Telescope (LAT) during the observatory’s initial year in space. The first challenge was eliminating emissions from our own galaxy.
“The extragalactic background is very faint, and it’s easily confused with the bright emission from the Milky Way,” said Markus Ackermann, another member of the Fermi LAT team at KIPAC who led the measurement study. “We have done a very careful job in separating the two components to determine the background’s absolute level.”
A separate paper describing the background measurement will appear in the March 12 issue of the journal Physical Review Letters.
Ajello and his colleagues then compared emissions from active galaxies that Fermi detected directly against the number needed to produce the observed extragalactic background. Between energies of 0.1 and 100 billion electron volts (GeV) – or from about 100 million to 30 billion times the energy of visible light – active galaxies turn out to be only minor players.
So, what else may contribute to the extragalactic gamma-ray background? “Particle acceleration occurring in normal star-forming galaxies is a strong contender,” Ackermann explained. “So is particle acceleration during the final assembly of the large-scale structure we observe today, for example, where clusters of galaxies are merging together.”
And there’s always dark matter, the mysterious substance that neither produces nor obscures light but whose gravity corrals normal matter. “Dark matter may be a type of as-yet-unknown subatomic particle. If that’s true, dark matter particles may interact with each other in a way that produces gamma rays,” Ajello added.
Improved analysis and extra sky exposure will enable the Fermi team to address these potential contributions. For now, though, the best that can be said about the extragalactic gamma-ray background is: Here, there be dragons.
By Francis Reddy
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md.