When the United States set a goal of landing a man on the moon, NASA Langley Research Center tackled the many challenges of spaceflight, trained astronauts, managed Project Mercury, and assumed major roles in both the Gemini and Apollo programs. Langley led the Lunar Orbiter initiative, which not only mapped the moon, but chose the spot for the first human landing. Langley aerospace engineer John Houbolt championed the lunar-orbit rendezvous concept, enabling the Apollo 11 moon landing and the safe return of its crew to Earth.
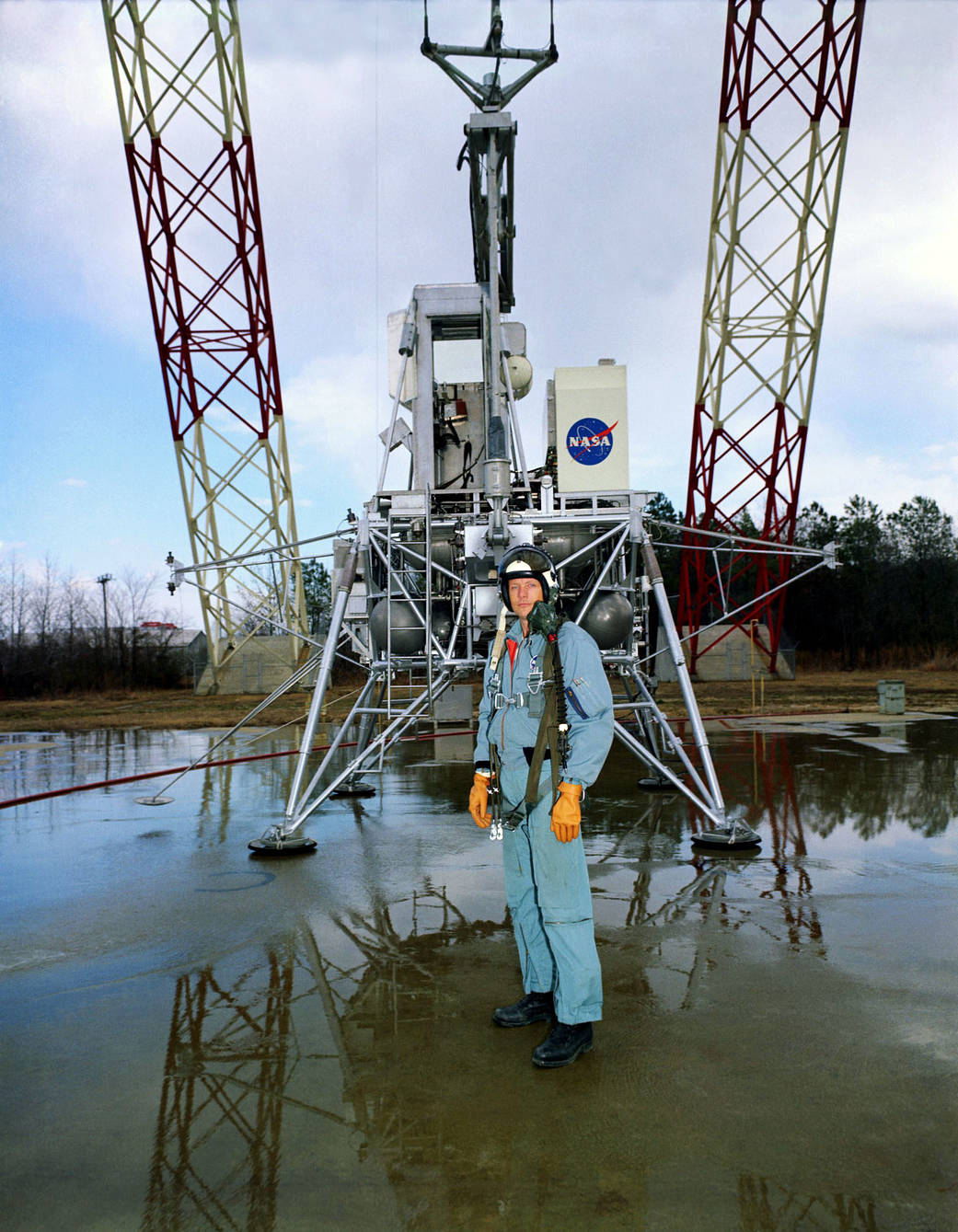
Neil Armstrong, the first human to set foot on the lunar surface, trained at Langley’s Lunar Landing Research Facility on equipment that cancelled all but one-sixth of Earth’s gravitational force to match that of the moon’s. This photograph shows Armstrong at the Lunar Landing Research Facility on Feb. 12, 1969. Twenty-four astronauts practiced touchdowns at the facility, where overhead cables supported five-sixths of the weight of a full-size model lander, and thrust was provided by a working rocket engine.
Part of the landing facility was the Reduced Gravity Simulator, which was attached to an overhead, lightweight trolley track. There, suspended on one side by a network of slings and cables, an astronaut’s ability to walk, run, and perform the various tasks required during lunar excursions was evaluated.
Armstrong offered what was perhaps the greatest tribute to the importance of his Langley training in Apollo 11’s success. When asked what it was like to land on the moon, he replied: “Like Langley.”
More: NASA Langley 100 – A Storied Legacy, A Soaring Future
Image Credit: NASA