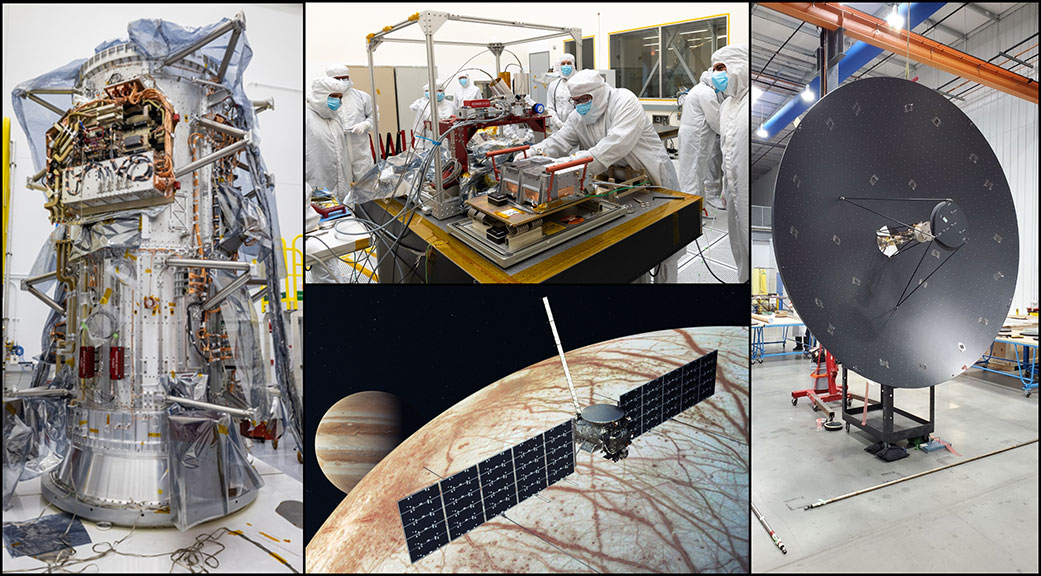
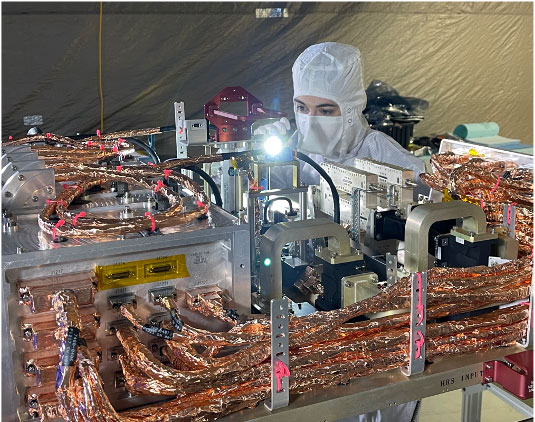
Science instruments and other hardware for the spacecraft will come together in the mission’s final phase before a launch to Jupiter’s icy moon Europa in 2024.
When it’s fully assembled, NASA’s Europa Clipper will be as large as an SUV with solar arrays long enough to span a basketball court – all the better to help power the spacecraft during its journey to Jupiter’s icy moon Europa. And just about every detail of the spacecraft will have been hand-crafted.
The assembly effort is already underway in clean rooms at the agency’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. Now, engineering components and science instruments are beginning to stream in from across the country and Europe. Before year’s end, most of the flight hardware – including a suite of nine science instruments – is expected to be complete.
The main body of the spacecraft is a giant 10-foot-tall (3-meter-tall) propulsion module, designed and constructed by Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland, with help from NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, and JPL. The module, fitted with electronics, radios, cabling, and the propulsion subsystem, will ship to JPL this spring. Europa Clipper’s 10-foot-wide (3-meter-wide) high-gain antenna also will be arriving at the Lab soon.
“We’re moving into the phase where we see the pieces all come together as a flight system,” said Europa Clipper Project Manager Jan Chodas of JPL. “It will be very exciting to see the hardware, the flight software, and the instruments get integrated and tested. To me, it’s the next level of discovery. We’ll learn how the system we designed will actually perform.”

Europa, which scientists are confident harbors an internal ocean with twice the amount of water in Earth’s oceans combined, may currently have conditions suitable for supporting life. Europa Clipper will orbit Jupiter and conduct multiple close flybys of Europa to gather data on the moon’s atmosphere, surface, and interior. Its sophisticated payload will investigate everything from the depth and salinity of the ocean to the thickness of the ice crust to the characteristics of potential plumes that may be venting subsurface water into space.
The first science instrument to be completed was delivered to JPL last week by a team at Southwest Research Institute in San Antonio, Texas. The ultraviolet spectrograph, called Europa-UVS, will search above the surface of Europa for signs of plumes. The instrument collects ultraviolet light, then separates the wavelengths of that light to help determine the composition of the moon’s surface and gases in the atmosphere.
As each instrument arrives at JPL, it will be integrated with the spacecraft and re-tested. Engineers need to be sure the instruments can communicate with the flight computer, spacecraft software, and the power subsystem.
Once all the components have been integrated to form the large flight system, Europa Clipper will move to JPL’s enormous thermal vacuum chamber for testing that simulates the harsh environment of deep space. There also will be intense vibration testing to ensure Europa Clipper can withstand the jostling of launch. Then it’s off to Cape Canaveral, Florida, for an October 2024 launch.
For the leaders of this mission, seeing the engineering components come together with the fleet of instruments will be especially moving, knowing how hard their teams have pushed to work through the coronavirus pandemic.
“I don’t know how I’ll feel, seeing this come together. I suspect it will be somewhat overwhelming,” said JPL’s Robert Pappalardo, the Europa Clipper project scientist. “It’s happening – it’s becoming real. It’s becoming tangible.”
At the same time, the level of difficulty kicks up several notches as the layers of the project merge.
“All of the parallel paths of hardware and software development will start to join together in a way that’s very visible to the team,” said JPL’s Jordan Evans, the deputy project manager. “Everybody’s eyes turn toward the integrated system that’s coming together, which is exciting.”
More About the Mission
Missions such as Europa Clipper contribute to the field of astrobiology, the interdisciplinary research on the variables and conditions of distant worlds that could harbor life as we know it. While Europa Clipper is not a life-detection mission, it will conduct detailed reconnaissance of Europa and investigate whether the icy moon, with its subsurface ocean, has the capability to support life. Understanding Europa’s habitability will help scientists better understand how life developed on Earth and the potential for finding life beyond our planet.
Managed by Caltech in Pasadena, California, JPL leads the development of the Europa Clipper mission in partnership with APL for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The Planetary Missions Program Office at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, executes program management of the Europa Clipper mission.
More information about Europa can be found here:
Gretchen McCartney
Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif.
818-393-6215
gretchen.p.mccartney@jpl.nasa.gov
Karen Fox / Alana Johnson
NASA Headquarters, Washington
301-286-6284 / 202-358-1501
karen.c.fox@nasa.gov / alana.r.johnson@nasa.gov
2022-023