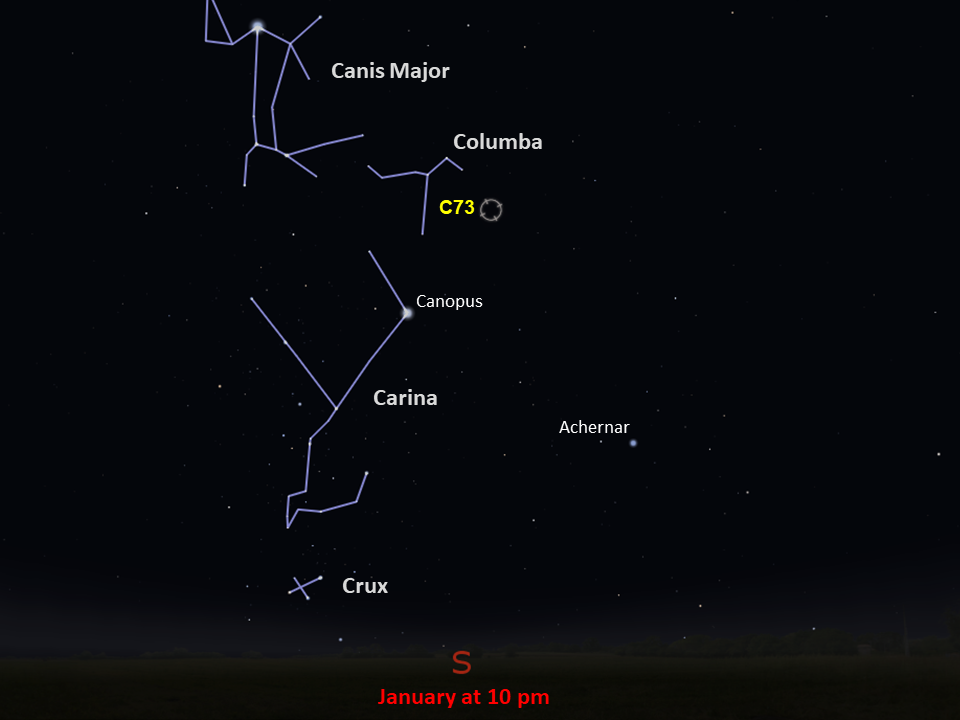
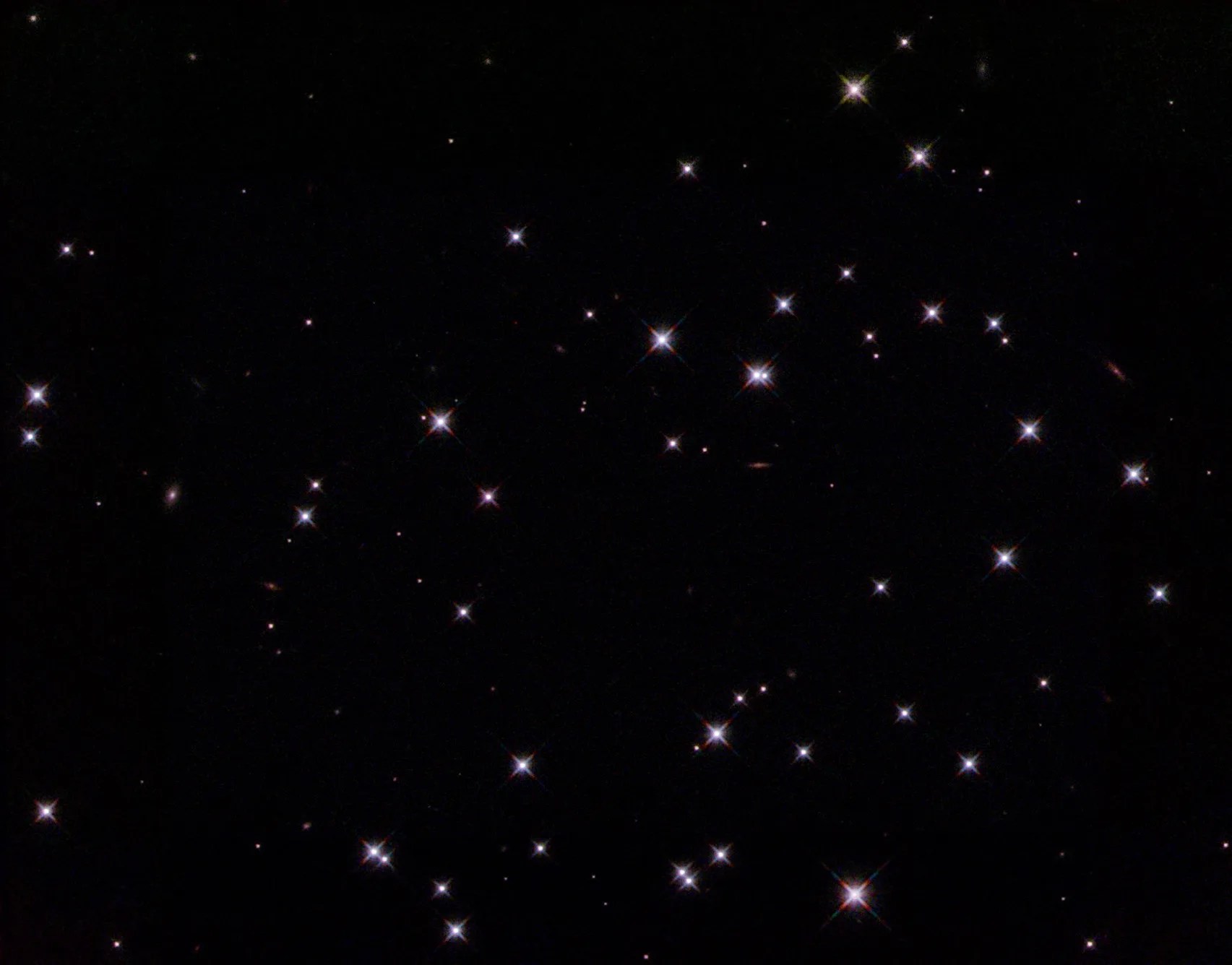
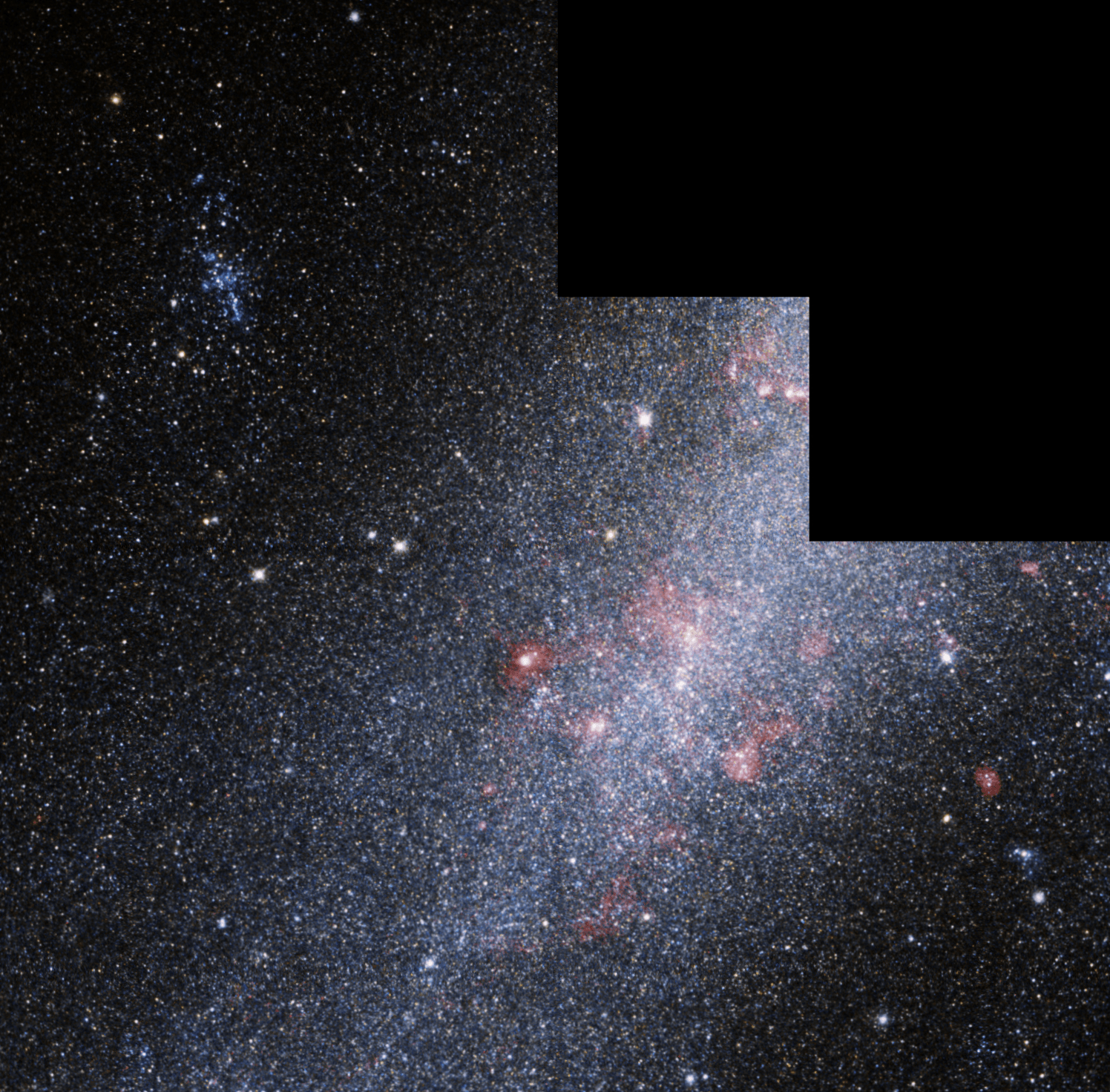
Caldwell 73
Caldwell 73 may be a remnant of two clusters that collided within a dwarf galaxy that once hosted them both.
Distance
40,000 light-years
Apparent Magnitude
7.3
constellation
Columba
object type
Globular Cluster
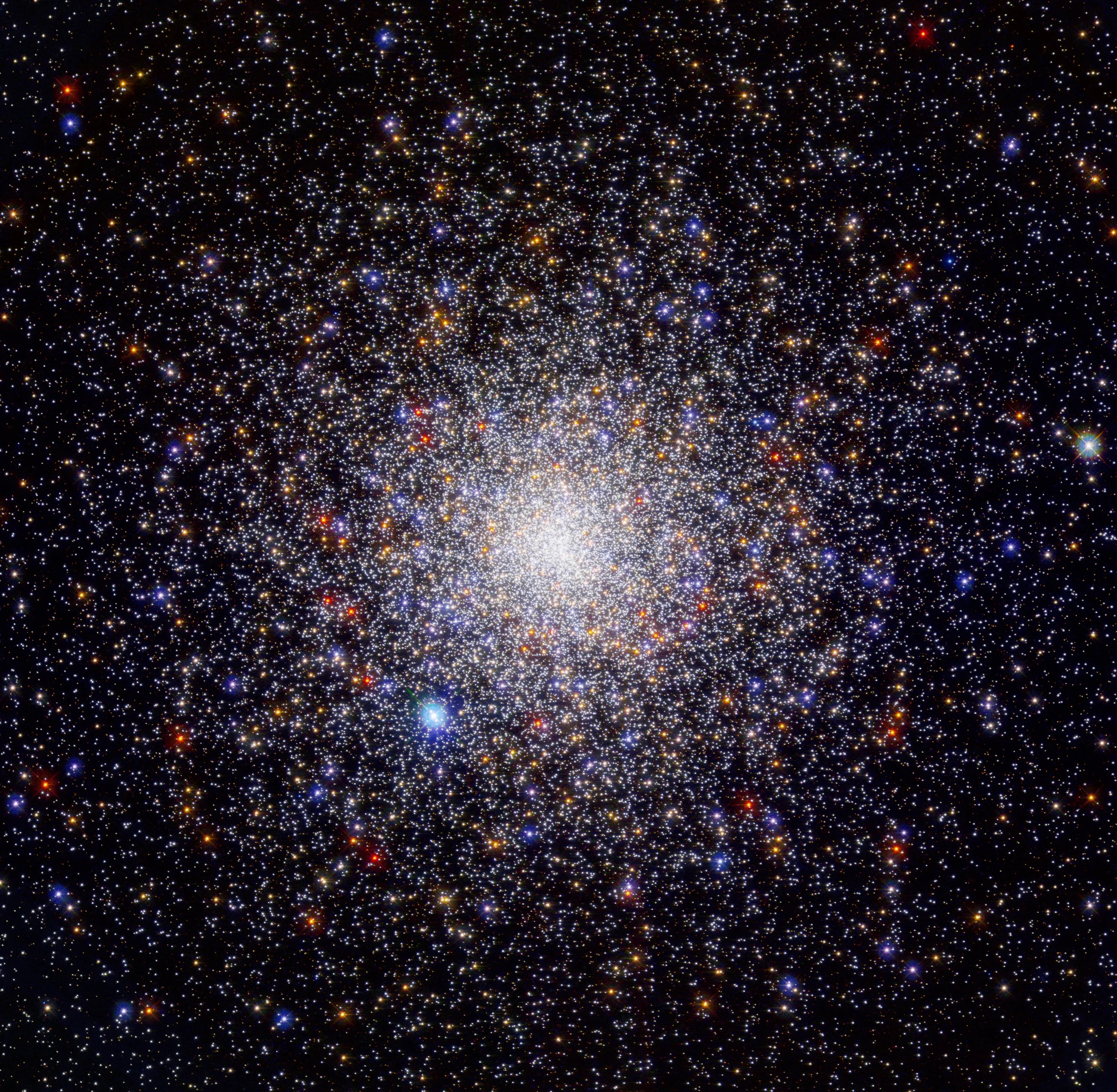

Caldwell 73, or NGC 1851, was discovered by the Scottish astronomer James Dunlop in 1826. It is located roughly 40,000 light-years from Earth in the constellation Columba and has an apparent magnitude of 7.3. This dense globular cluster can be spotted through a pair of binoculars, appearing as a fuzzy patch of light. Small telescopes will resolve some of the cluster’s individual stars, away from its compact center. Caldwell 73 is easiest to view from equatorial latitudes in the Northern Hemisphere during the winter and from the Southern Hemisphere during the summer.
The stars in many known globular clusters are about the same age, indicating that the stars formed at roughly the same time. However, observations of Caldwell 73 reveal that it hosts stellar populations with different ages. The cluster is also encircled by a diffuse halo of stars. Although the origins of the halo and multiple star populations are unknown, one idea is that Caldwell 73 is a remnant of two clusters that collided within a dwarf galaxy that once hosted them both. When the clusters merged, the outer regions of the host galaxy may have been stripped away via interactions with more massive galaxies, leaving only the stellar nucleus and halo behind.
This image of Caldwell 73 was captured by Hubble’s Wide Field Camera 3. It is a composite of multiple observations taken at ultraviolet and visible wavelengths. The observations were taken to help astronomers better understand why some globular clusters appear to play host to multiple generations of stars. A bright, blue, giant star appears to the lower left of center.
Glossary
Apparent Magnitude - The brightness of an astronomical object as seen from Earth, influenced by the object's distance from Earth, its absolute magnitude, and even gas and dust that lie between the object and Earth.
Globular Cluster - A spherical group of stars that are gravitationally bound to each other, with most of the stars concentrated at the cluster’s center.
Explore Hubble's Caldwell Catalog
The following pages contain some of Hubble’s best images of Caldwell objects.

Caldwell 1
Also known as NGC 188, this group of stars formed from a large cloud of gas making the stars roughly…

Caldwell 2
This shell of gas is expanding outward, away from the dying star within.
Caldwell 3
This barred spiral galaxy was first spotted by British astronomer William Herschel in April 1793 in the constellation Draco.




