6 min read
Astronomers using NASA's Hubble Space Telescope watched a mysterious dark vortex on Neptune abruptly steer away from a likely death on the giant blue planet.
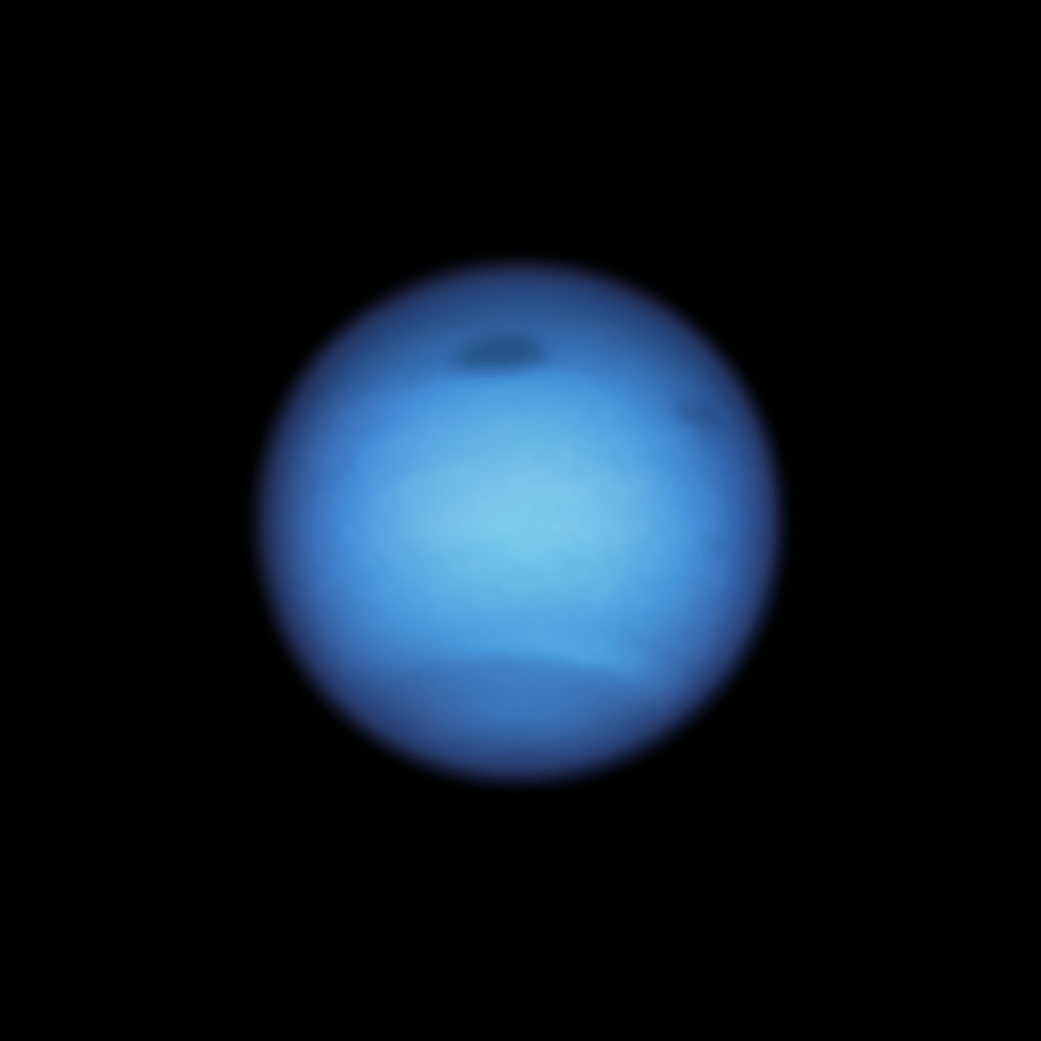
The storm, which is wider than the Atlantic Ocean, was born in the planet's northern hemisphere and discovered by Hubble in 2018. Observations a year later showed that it began drifting southward toward the equator, where such storms are expected to vanish from sight. To the surprise of observers, Hubble spotted the vortex change direction by August 2020, doubling back to the north. Though Hubble has tracked similar dark spots over the past 30 years, this unpredictable atmospheric behavior is something new to see.
Equally as puzzling, the storm was not alone. Hubble spotted another, smaller dark spot in January this year that temporarily appeared near its larger cousin. It might possibly have been a piece of the giant vortex that broke off, drifted away, and then disappeared in subsequent observations.
"We are excited about these observations because this smaller dark fragment is potentially part of the dark spot’s disruption process," said Michael H. Wong of the University of California at Berkeley. "This is a process that's never been observed. We have seen some other dark spots fading away, and they're gone, but we've never seen anything disrupt, even though it’s predicted in computer simulations."
The large storm, which is 4,600 miles across, is the fourth dark spot Hubble has observed on Neptune since 1993. Two other dark storms were discovered by the Voyager 2 spacecraft in 1989 as it flew by the distant planet, but they had disappeared before Hubble could observe them. Since then, only Hubble has had the sharpness and sensitivity in visible light to track these elusive features, which have sequentially appeared and then faded away over a duration of about two years each. Hubble uncovered this latest storm in September 2018.
Wicked Weather
Neptune's dark vortices are high-pressure systems that can form at mid-latitudes and may then migrate toward the equator. They start out remaining stable due to Coriolis forces, which cause northern hemisphere storms to rotate clockwise, due to the planet's rotation. (These storms are unlike hurricanes on Earth, which rotate counterclockwise because they are low-pressure systems.) However, as a storm drifts toward the equator, the Coriolis effect weakens and the storm disintegrates. In computer simulations by several different teams, these storms follow a more-or-less straight path to the equator, until there is no Coriolis effect to hold them together. Unlike the simulations, the latest giant storm didn't migrate into the equatorial "kill zone."
"It was really exciting to see this one act like it's supposed to act and then all of a sudden it just stops and swings back," Wong said. "That was surprising."
Dark Spot Jr.
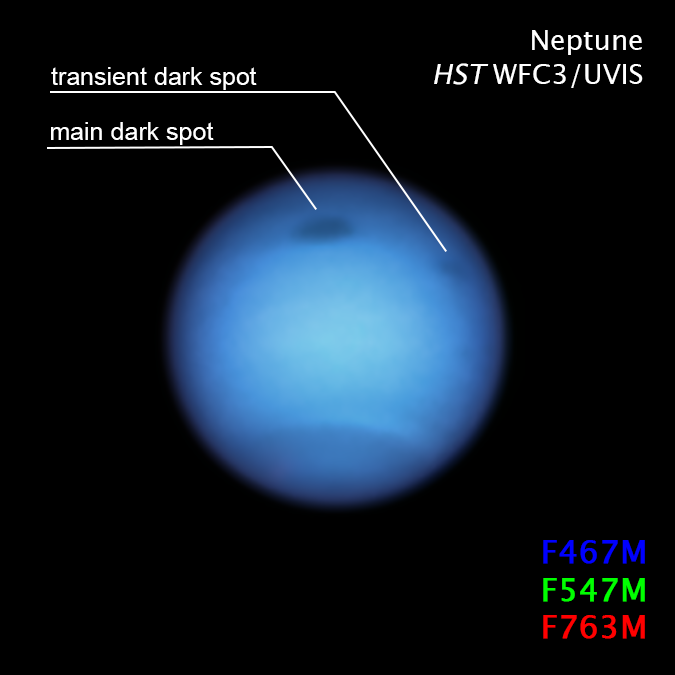

The Hubble observations also revealed that the dark vortex’s puzzling path reversal occurred at the same time that a new spot, informally deemed "dark spot jr.," appeared. The newest spot was slightly smaller than its cousin, measuring about 3,900 miles across. It was near the side of the main dark spot that faces the equator — the location that some simulations show a disruption would occur.
However, the timing of the smaller spot's emergence was unusual. "When I first saw the small spot, I thought the bigger one was being disrupted," Wong said. "I didn't think another vortex was forming because the small one is farther towards the equator. So it's within this unstable region. But we can't prove the two are related. It remains a complete mystery.
"It was also in January that the dark vortex stopped its motion and started moving northward again," Wong added. "Maybe by shedding that fragment, that was enough to stop it from moving towards the equator."
The researchers are continuing to analyze more data to determine whether remnants of dark spot jr. persisted through the rest of 2020.
Dark Storms Still Puzzling
It's still a mystery how these storms form, but this latest giant dark vortex is the best studied so far. The storm's dark appearance may be due to an elevated dark cloud layer, and it could be telling astronomers about the storm's vertical structure.
Another unusual feature of the dark spot is the absence of bright companion clouds around it, which were present in Hubble images taken when the vortex was discovered in 2018. Apparently, the clouds disappeared when the vortex halted its southward journey. The bright clouds form when the flow of air is perturbed and diverted upward over the vortex, causing gases to likely freeze into methane ice crystals. The lack of clouds could be revealing information on how spots evolve, say researchers.
Weather Eye on the Outer Planets
Hubble snapped many of the images of the dark spots as part of the Outer Planet Atmospheres Legacy (OPAL) program, a long-term Hubble project, led by Amy Simon of NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, that annually captures global maps of our solar system's outer planets when they are closest to Earth in their orbits.
OPAL's key goals are to study long-term seasonal changes, as well as capture comparatively transitory events, such as the appearance of dark spots on Neptune or potentially Uranus. These dark storms may be so fleeting that in the past some of them may have appeared and faded during multi-year gaps in Hubble's observations of Neptune. The OPAL program ensures that astronomers won't miss another one.
Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
"We wouldn't know anything about these latest dark spots if it wasn't for Hubble," Simon said. "We can now follow the large storm for years and watch its complete life cycle. If we didn't have Hubble, then we might think the Great Dark Spot seen by Voyager in 1989 is still there on Neptune, just like Jupiter's Great Red Spot. And, we wouldn't have known about the four other spots Hubble discovered." Wong will present the team's findings Dec. 15 at the fall meeting of the American Geophysical Union.
The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and ESA (European Space Agency). NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, Maryland, conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy in Washington, D.C.
Media Contacts:
Claire Andreoli
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
301-286-1940
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov
Donna Weaver / Ray Villard
Space Telescope Science Institute, Baltimore, Maryland
410-338-4493 / 410-338-4514
dweaver@stsci.edu / villard@stsci.edu
Science Contacts:
Michael H. Wong
University of California, Berkeley, California
mikewong@astro.berkeley.edu
Amy Simon
NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Maryland
amy.simon@nasa.gov







