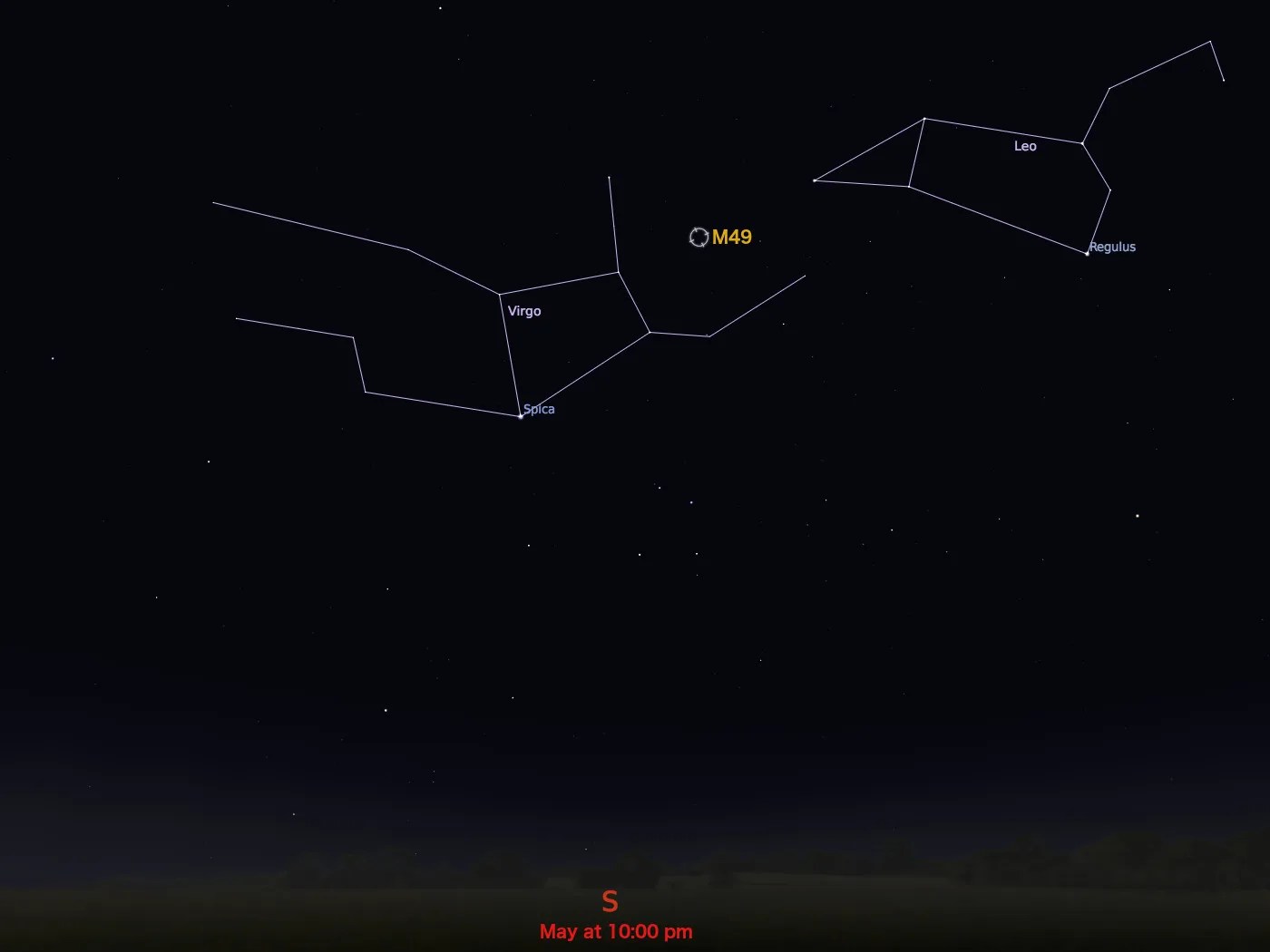
Messier 49
Messier 49 holds nearly 6,000 globular clusters.
Distance
60 million light-years
Apparent Magnitude
9.4
constellation
Virgo
object type
Elliptical Galaxy
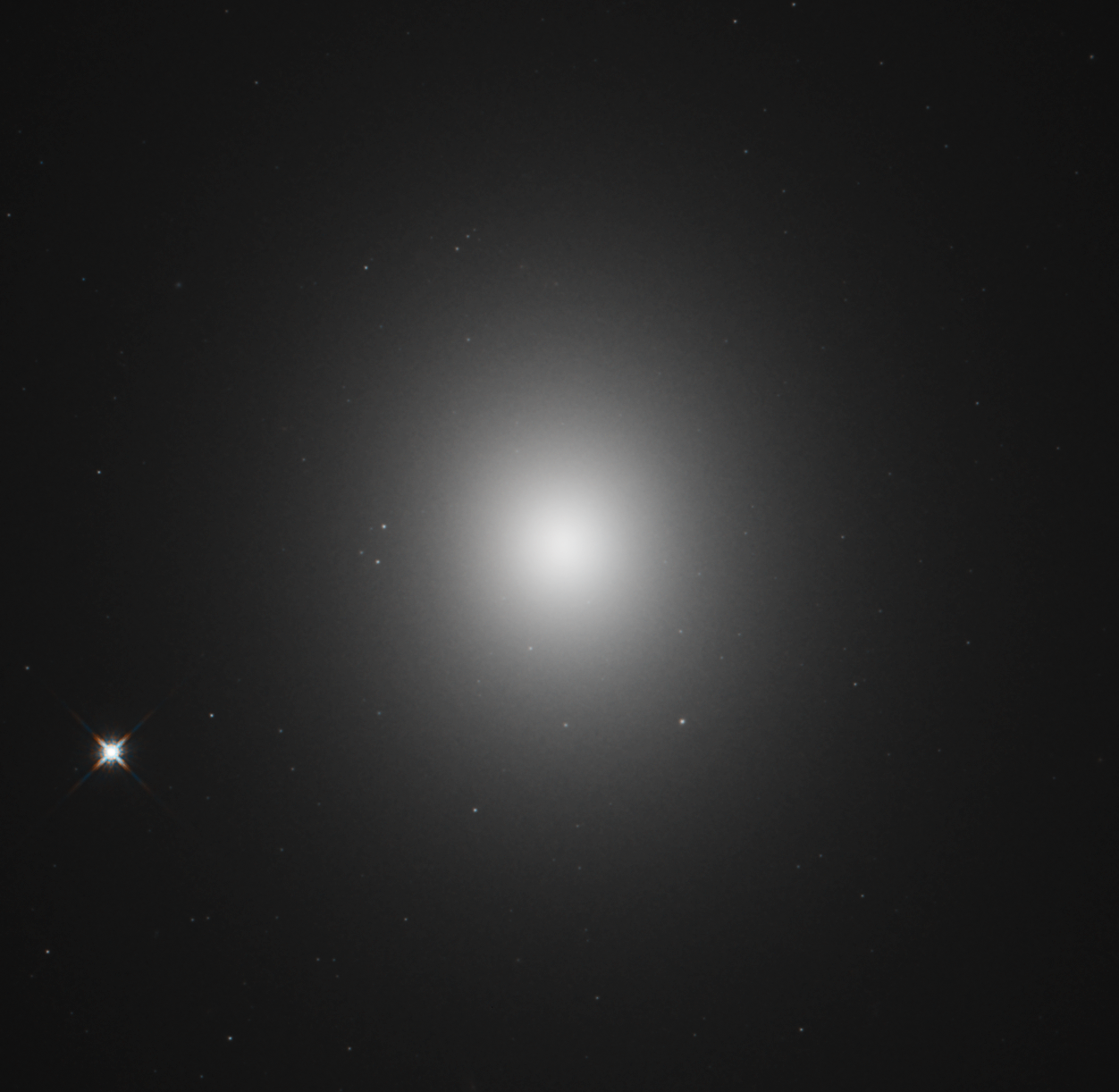

The elliptical galaxy M49 was discovered by Charles Messier in 1771. Not only was it the first object discovered in the Virgo Cluster of galaxies, but it was also the first elliptical galaxy detected outside of the Milky Way’s Local Group. Unlike spiral galaxies that have well-defined structures and picturesque spiral arms, elliptical galaxies are fairly featureless with little structure. The stars in elliptical galaxies are usually much older than those in spiral galaxies. M49 also contains a rich collection of globular star clusters — nearly 6,000.
This Hubble image of M49 was created using observations at infrared wavelengths. There is an X-ray source at the core of the galaxy, indicating that a supermassive black hole lurks at the center of M49. The estimated mass of this supermassive black hole is roughly 565 million times the mass of our sun.
M49 is located 60 million light-years from Earth in the constellation Virgo. It has an apparent magnitude of 9.4 and can be observed using a pair of binoculars. The best time to observe the galaxy is during the month of May.
For more information about Hubble’s observations of M49, see:
Explore Hubble's Messier Catalog
The following pages contain some of Hubble’s best images of Messier objects.
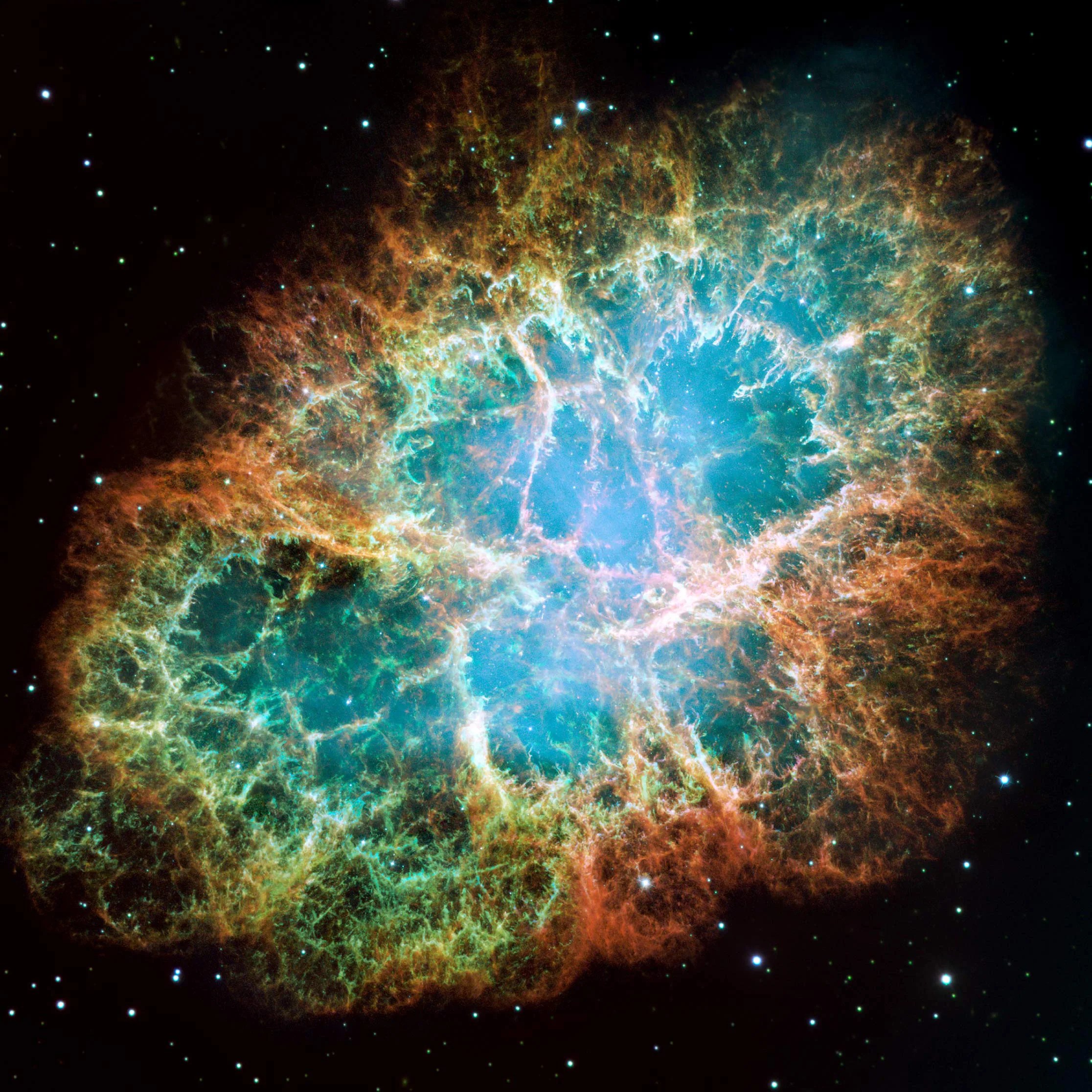

Messier 1 (The Crab Nebula)
Better known as the Crab Nebula, Charles Messier originally mistook Messier 1 for Halley’s Comet, which inspired him to create…
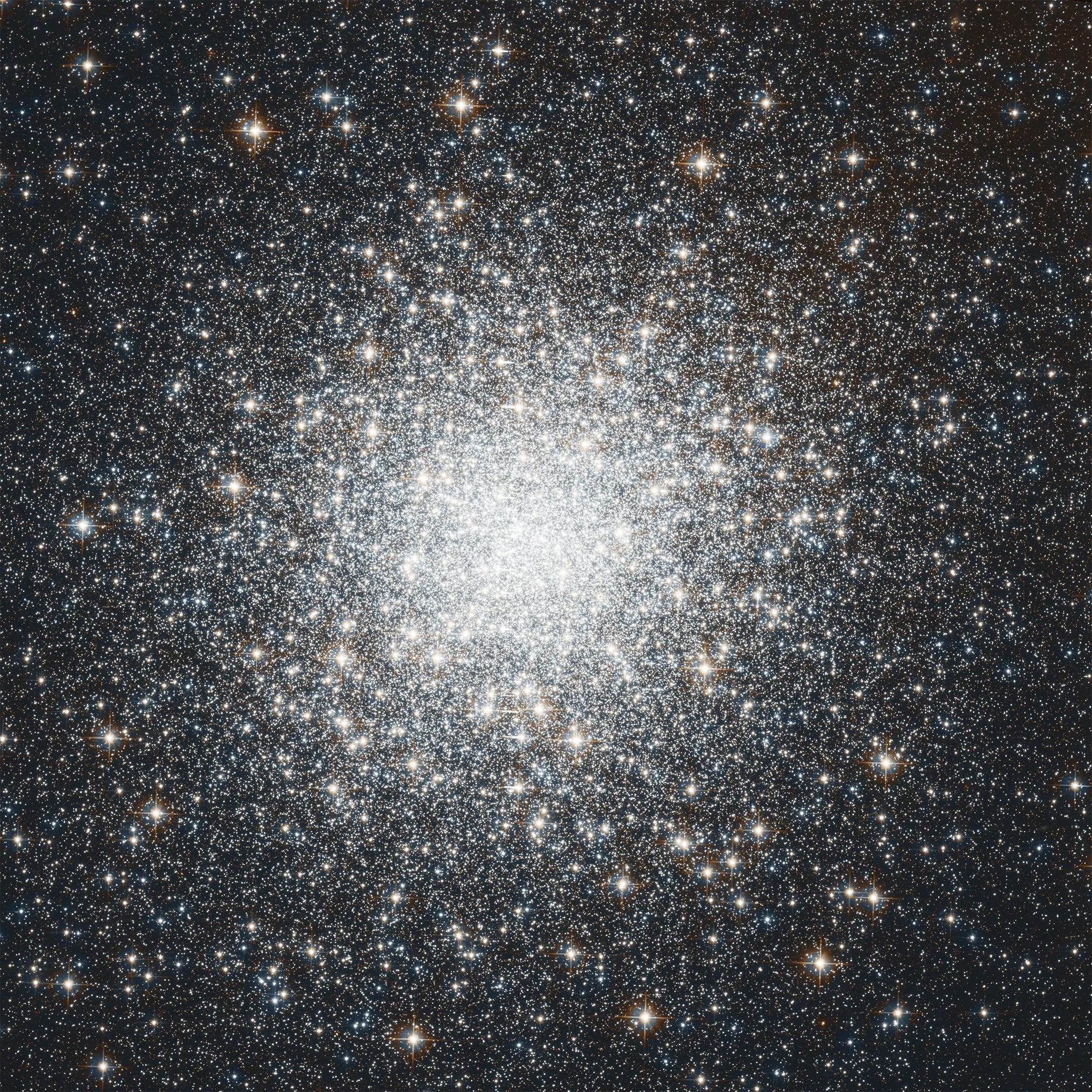

Messier 2
Hubble's image of Messier 2 is comprised of visible and infrared wavelengths of light.
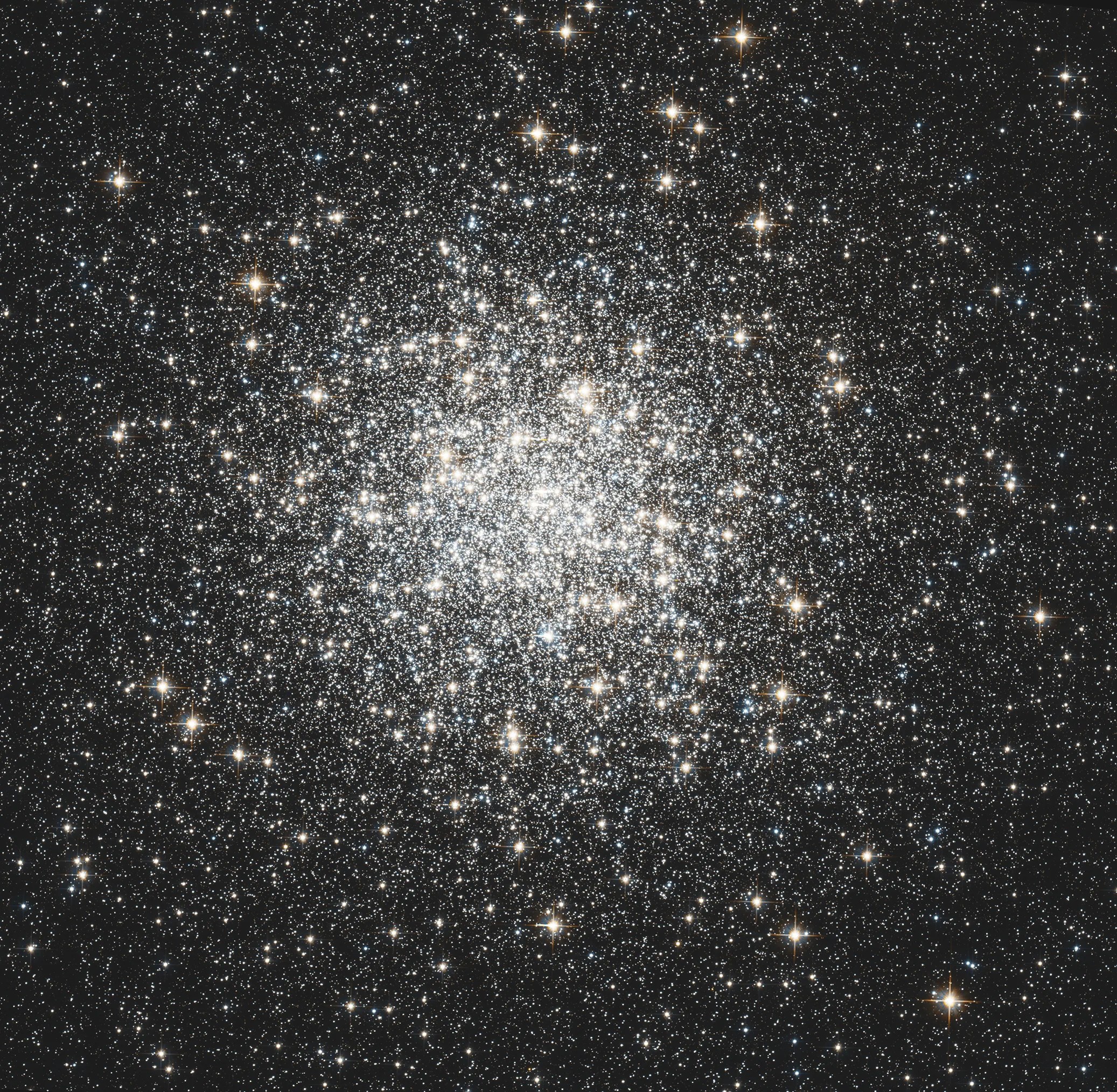

Messier 3
Messier 3 holds more than 500,000 stars.