1 min read
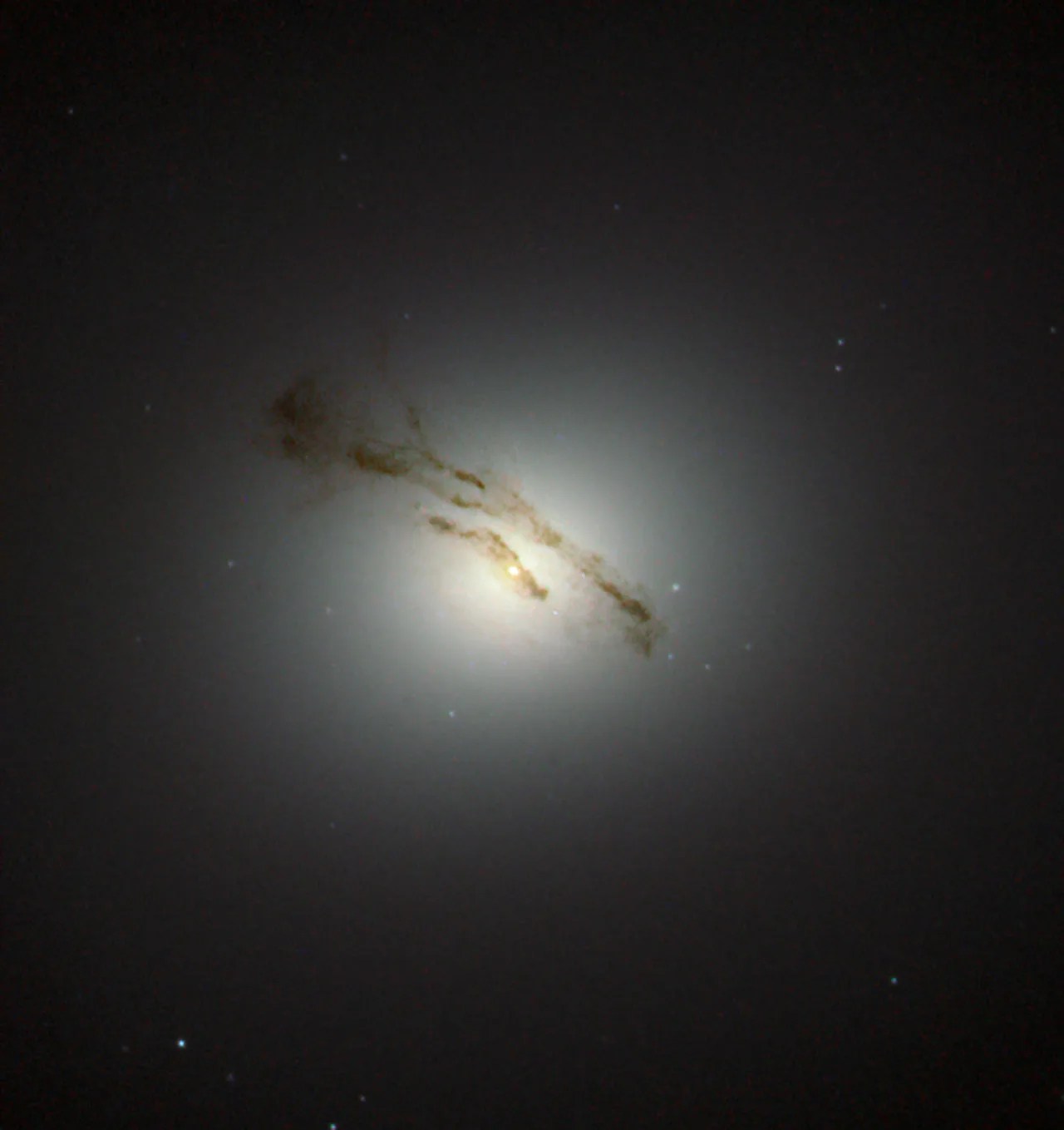

This elliptical galaxy was discovered in March 1781 and lies about 60 million light-years away from Earth in the constellation of Virgo (The Virgin). The galaxy is part of the very heavily populated center of the Virgo Cluster, a cluster which consists of more than 1,000 galaxies.
This image does not show the whole galaxy but only its very interesting center with intriguing dust lanes that stretch across it. This is likely to be the best image of the region ever captured. Previous observations using Hubble’s Space Telescope Imaging Spectrograph (STIS) revealed a supermassive black hole in the center of Messier 84. Astronomers found the supermassive black hole by mapping the motion of the gas and the stars which are caught in its grip.
Next to its interesting center Messier 84 is also known for its supernovae. Two supernovae have been observed within the galaxy. The first, SN1957, was discovered in 1957 and another, called SN1991bg, was discovered in 1991.
Text credit: European Space Agency