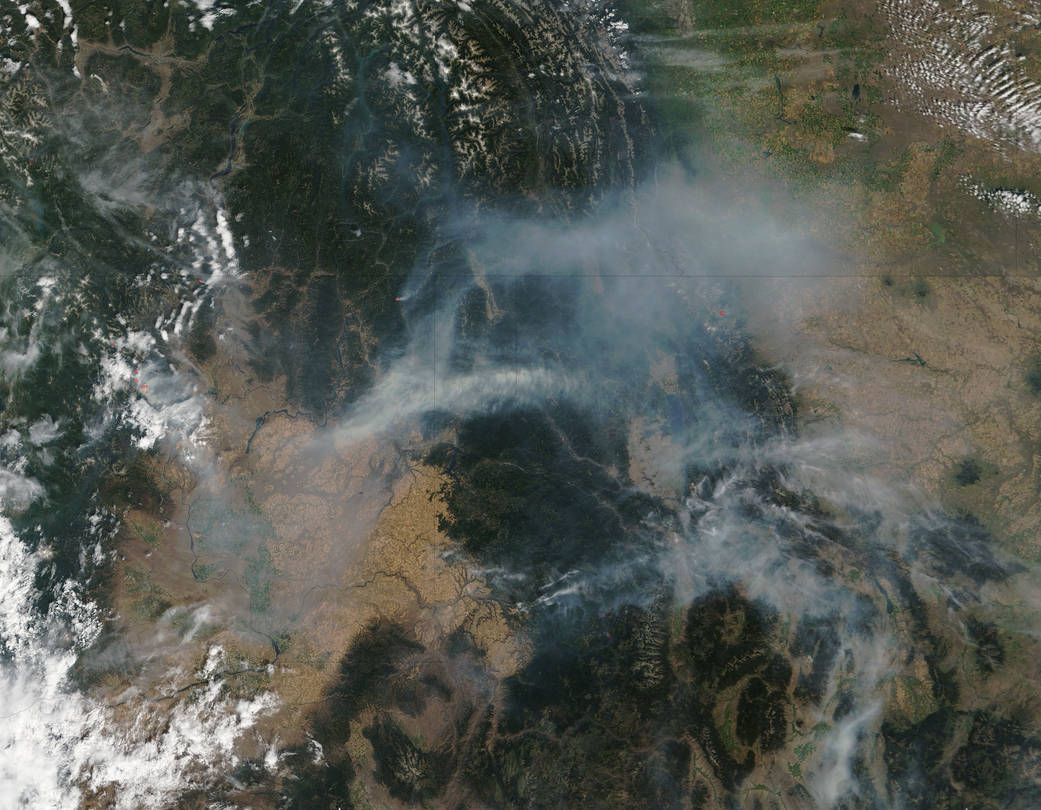
NASA’s Terra satellite spotted a large area of smoke from the Wolverine Fire that stretched over central and western Washington, northern Idaho and into western Montana.
According to InciWeb, the Wolverine Fire was burning on the west shore of Lake Chelan in the Mount Baker-Snoqualmie National Forest, located in the north-central part of the state. The fire experienced growth over the weekend of Aug. 1 and 2.
InciWeb is an interagency all-risk incident information management system that coordinates with federal, state and local agencies to manage wildfires. InciWeb reported that the fire began from a lightning strike on Monday, June 29, at approximately 7:30 a.m. EDT, about 3 miles northwest of Lucerne, Washington.
On Aug. 1, a huge plume of smoke generated from the Wolverine Fire in Chelan County was visible from the Spokane and Seattle area. According to InciWeb, by that night, the fire had expanded to 15,760 acres. The fire moved southwest along the lakeshore between the Twin Harbor and Little Creek drainages and northwest to Bridal Vail Creek. For fire updates, visit: http://inciweb.nwcg.gov/incident/4354/.
This satellite image shows the large plume of smoke from the Wolverine Fire on Aug. 2, 2015, at 19:15 UTC. The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument that flies onboard NASA’s Aqua satellite captured an image of smoke from these fires Aug. 2 at 21:05 UTC (5:05 p.m. EDT). The multiple red pixels are heat signatures (red) detected by MODIS. The smoke appears to be a light brown color.
A high pressure system located over the region of fire is causing an inversion. Smoke is heavy over the fire which creates poor visibility and safety concerns for firefighters.
Text credit: NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Rob Gutro
Image credit: NASA MODIS Rapid Response Team, Jeff Schmaltz.