Ice fronts have retreated, rocky peaks are more exposed, fewer icebergs drift to the ocean: the branching network of glaciers that empty into Greenland’s Sermilik Fjord has changed significantly in the last half century. Comparing Landsat images from 1972 and 2019, those changes and more come into view.
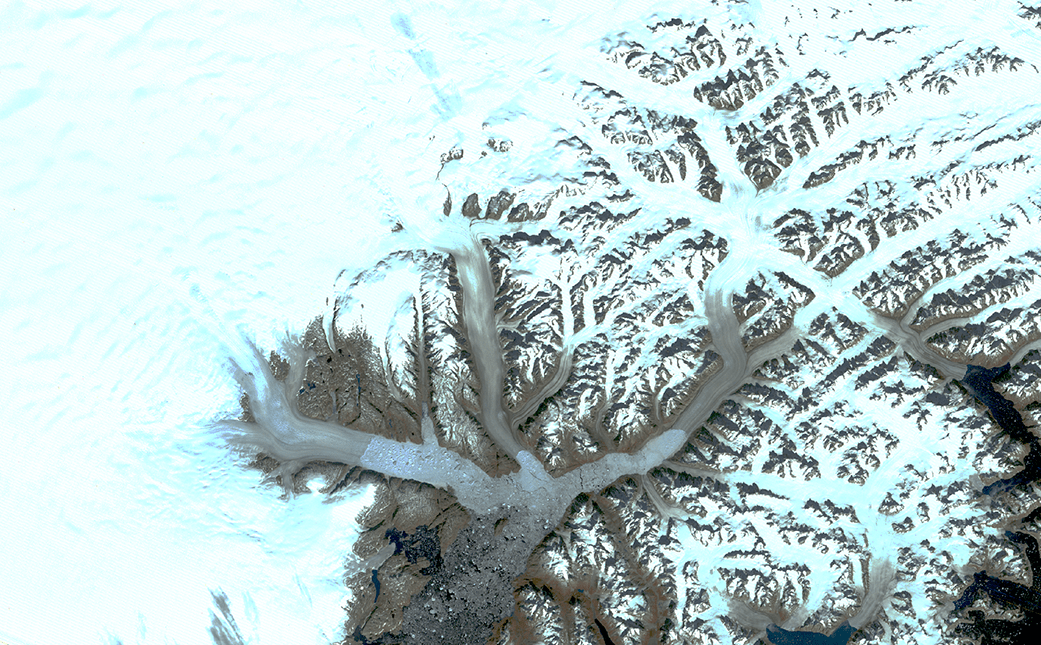
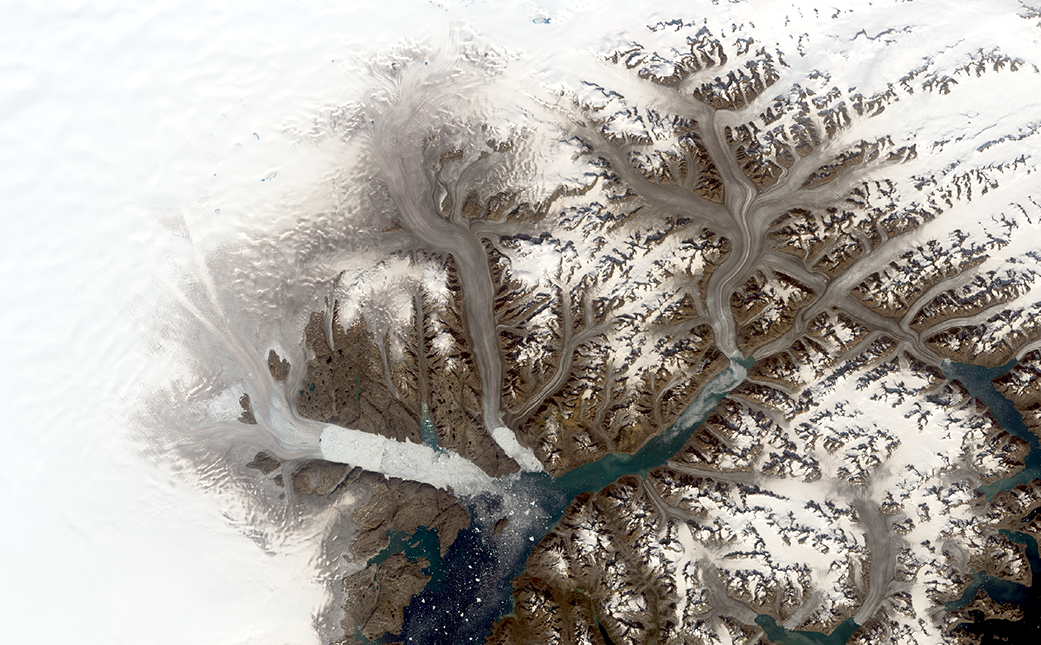


The glaciers appear brownish grey in this true-color Landsat 8 satellite image from Aug. 12, 2019. The color indicates that the surface has melted, a process that concentrates dust and rock particles and leads to a darker recrystallized ice sheet surface.
The darker melt surface in 2019 extends much farther onto the ice sheet than it did in 1972, when the first Landsat satellite gathered data on the area, said Christopher Shuman, a glaciologist with the University of Maryland, Baltimore County, at NASA Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. Landsat is a joint mission of NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.
Helheim Glacier, one of the largest and fastest flowing of its kind in Greenland, has retreated approximately 4.7 miles (7.5 kilometers) up a wide fjord in the time between the two scenes, leaving a jumble of sea ice where its calving front used to be. To the east, Midgard Glacier has retreated approximately 10 miles (16 kilometers), splitting into two branches farther up the fjord. Changes to the rocky outcrops of the area’s mountains and smaller tributary glaciers are also visible by comparing the two Landsat images.
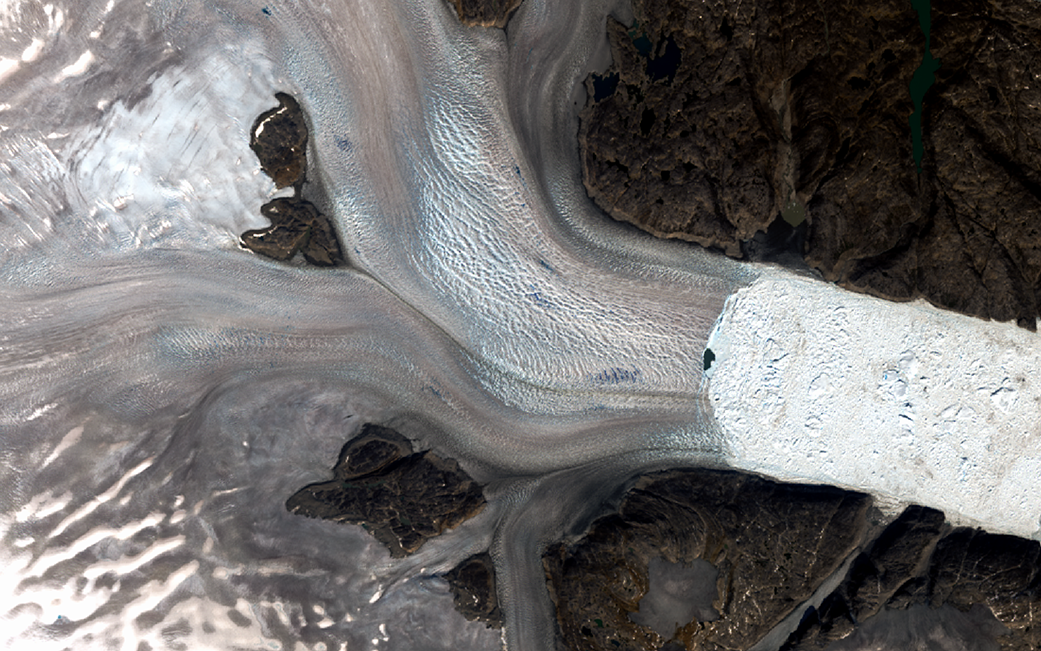
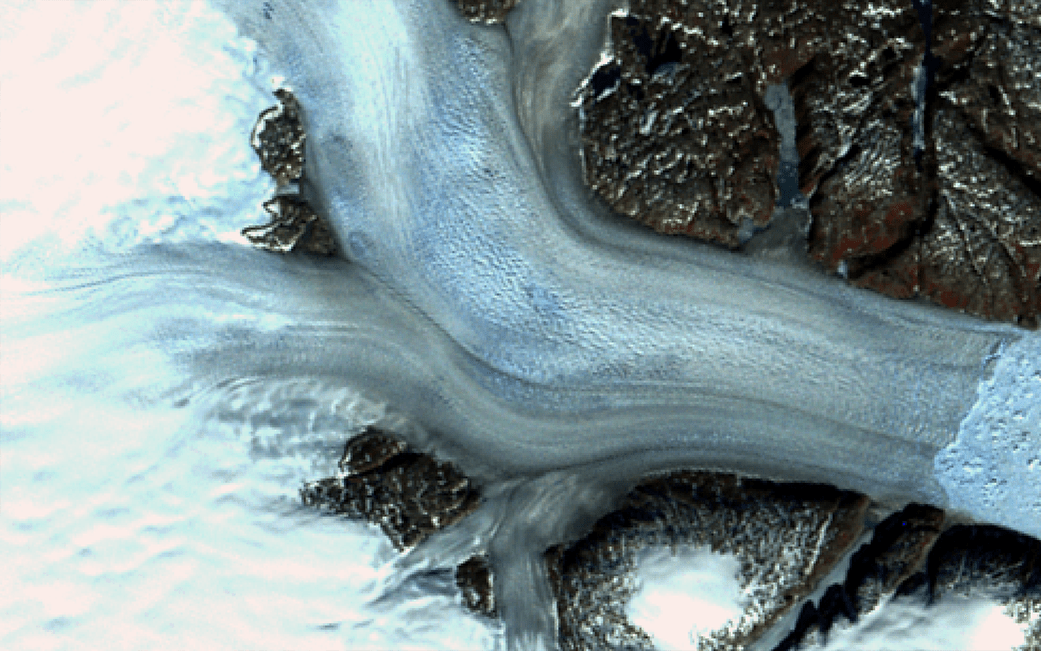

“There’s a lot more bare rock visible now, which used to be covered with ice,” Shuman said. “And all these little glaciers are all getting slammed, as well as the bigger ones like Helheim, Fenris and Midgard. There are scores of examples of change just in this one area.”
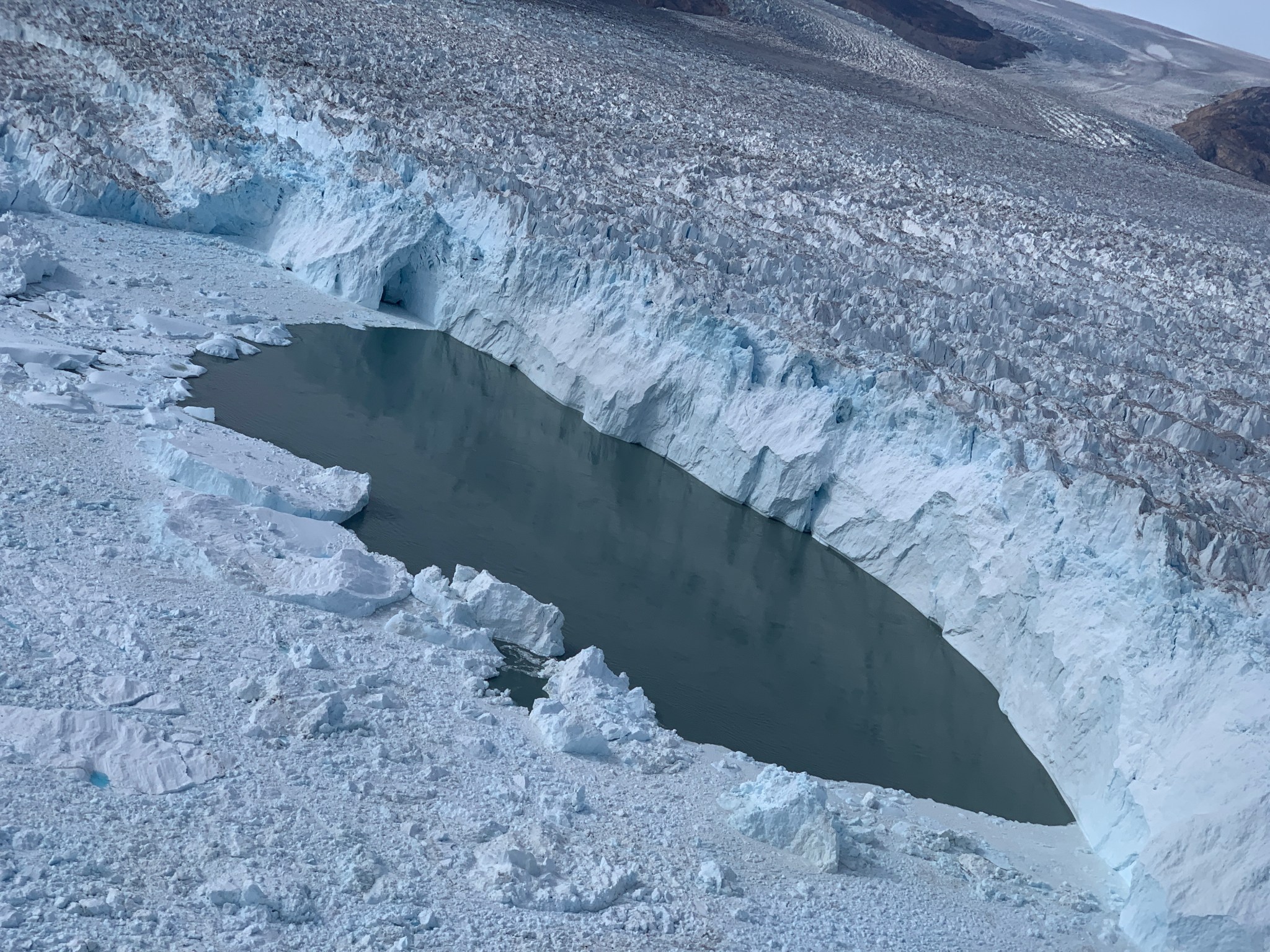
In a close-up of the Helheim Glacier, a patch of open water is visible right at the calving front. Three days after Landsat 8 collected the image over Helheim and its neighboring glaciers, NASA’s Oceans Melting Greenland (OMG) project flew over that open patch of water in an airplane and dropped a temperature-measuring probe that detected warm water at the ice front. OMG is examining how oceans melt glaciers from below, even as air temperatures warm the ice from above.

Unusually warm air temperatures this summer have caused record melt across Greenland. Approximately 90% of the surface of Greenland’s ice sheet melted at some point between July 30 and Aug. 2, during which time an estimated 55 billion tons of ice melted into the ocean, according to the National Snow and Ice Data Center. Shuman also tracked the unusual warm weather at the top of the Greenland Ice Sheet, 10,550 feet (3,216 meters) above sea level, where temperatures were above freezing for more than 16.5 hours total during July 30 and 31.
By: Kate Ramsayer
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md.

























