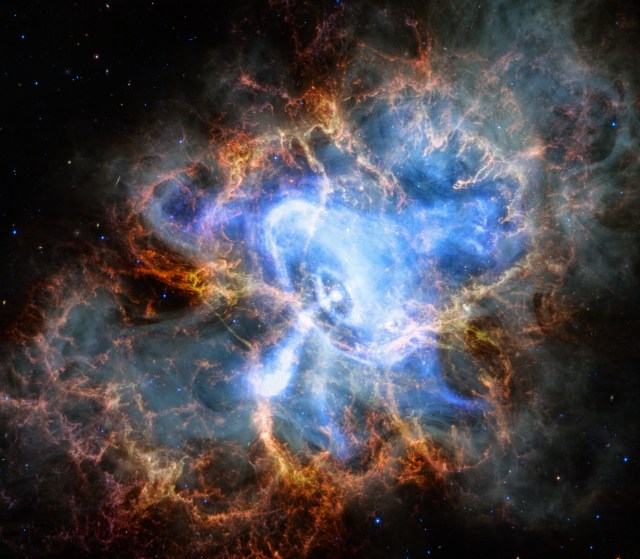
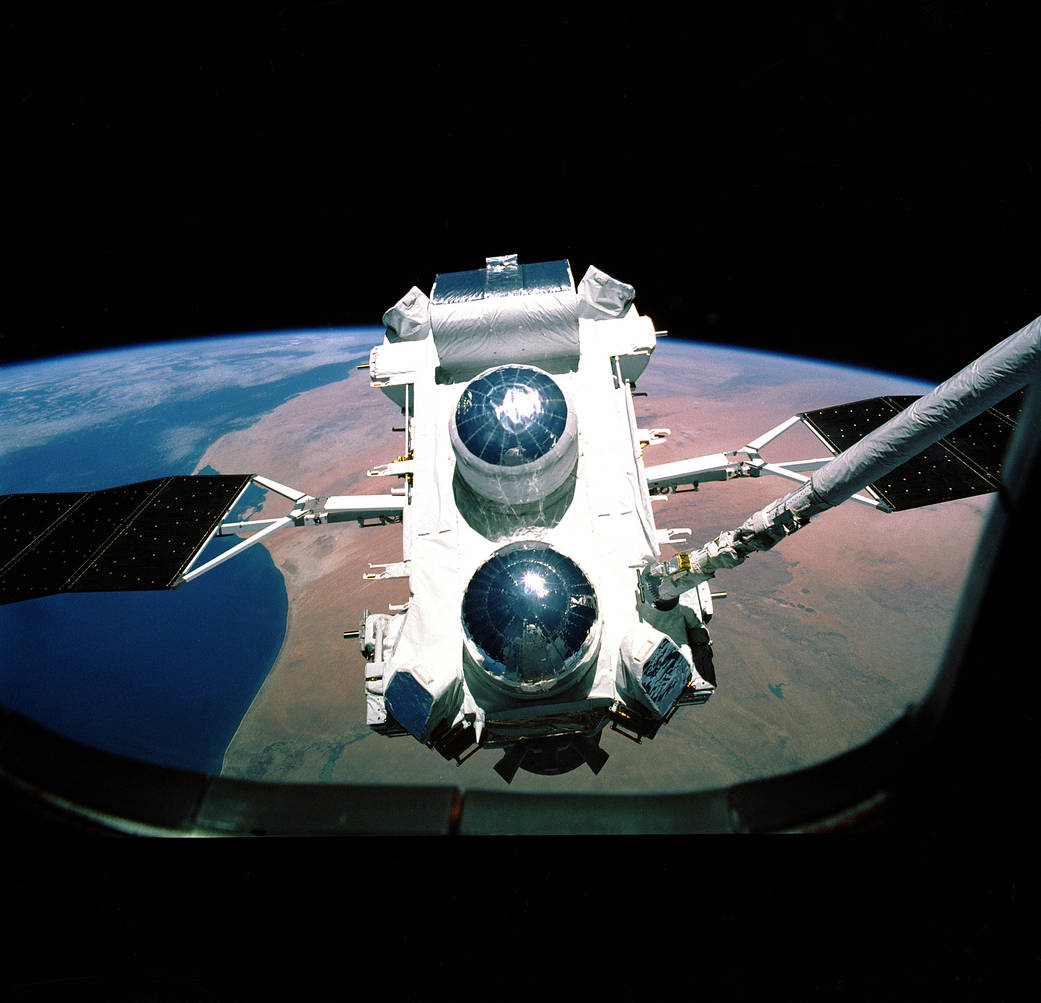
On April 5, 1991, the Compton Gamma-ray Observatory (CGRO) was launched aboard the Space Shuttle Atlantis from Kennedy Space Center. Named in honor of Nobel Prize winner, Dr. Arthur Holly Compton, CGRO was the second of NASA’s “Great Observatories” following the Hubble Space Telescope 1990 launch and was at the time of launch, the heaviest astrophysical payload ever flown on board the Shuttle. The purpose of the CGRO mission was to use its collection of four primary instruments to detect the broad range of high energy radiation known as gamma-rays. The Burst and Transient Source Experiment (BATSE) instrument, which served as the all-sky monitor for gamma-ray bursts on the observatory, was built in-house by NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Ala. The Principal Investigator (PI) for BATSE was Dr. Gerald J. Fishman, who in 2011, claimed a shared the Shaw Prize alongside Italian astronomer, Enrico Costa. The observatory was safely deorbited and re-entered the Earth’s atmosphere on June 4, 2000.
Image credit: NASA/MSFC